Icebergs are massive floating ice chunks that break off from glaciers or ice shelves. While they may appear as isolated ice masses, they play a crucial role in marine ecosystems. As they drift and melt, icebergs release fresh water and nutrients into the ocean, supporting various aquatic life forms. Their presence can influence ocean currents, water temperature, and salinity, affecting marine organisms’ distribution and health.
The World’s Largest Iceberg: A23a
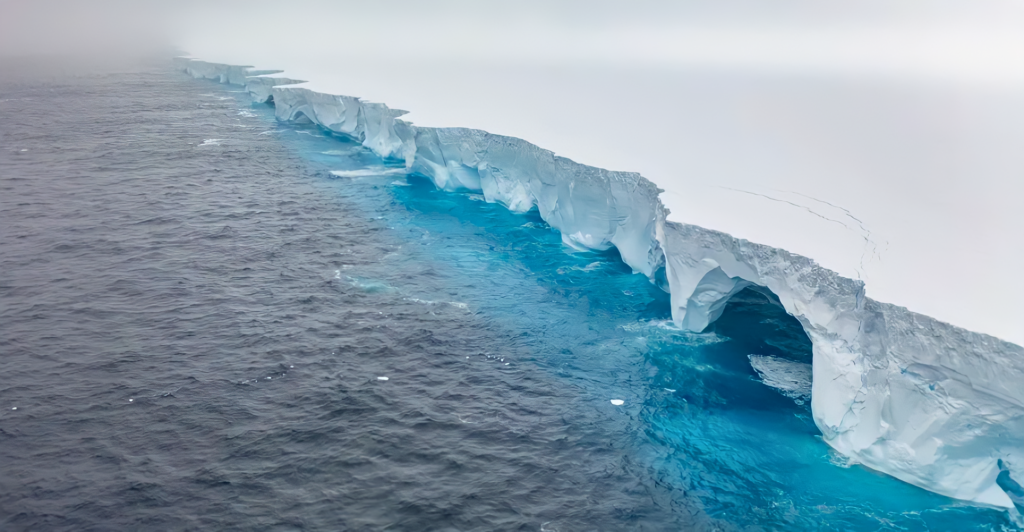

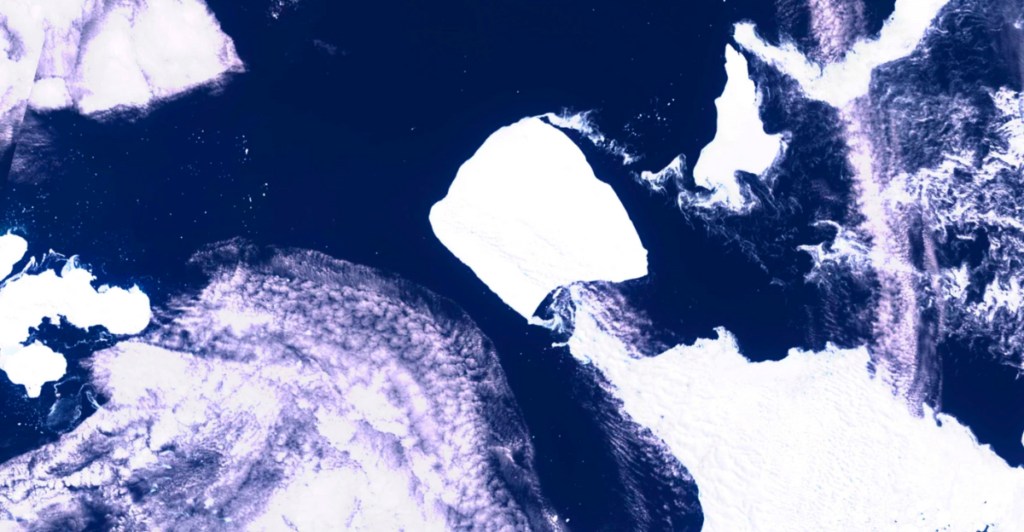
Iceberg A23a, currently the world’s largest iceberg, measures approximately 3,500 square kilometers, twice the size of Greater London. Originating from the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in Antarctica, A23a was grounded for over 30 years before recently breaking free. Its immense size and movement have garnered significant attention due to potential ecological impacts as it drifts through the Southern Ocean.
Potential Collision with South Georgia Island
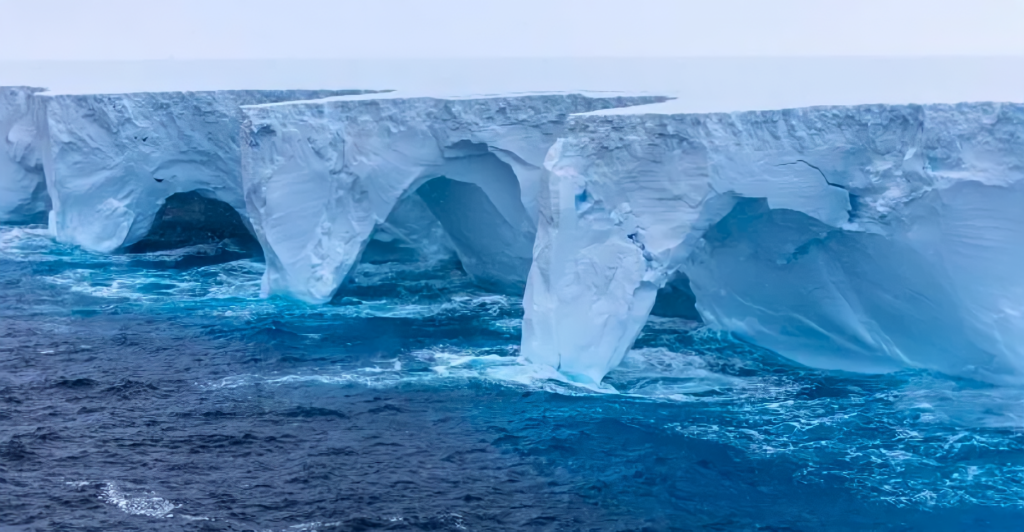

A23a is on a trajectory toward South Georgia Island, a remote British territory in the South Atlantic Ocean. This island is renowned for its rich biodiversity, including colonies of penguins, seals, and other marine life. Scientists are closely monitoring the iceberg’s path, as a collision could disrupt local ecosystems and the species that inhabit them.
Historical Precedents: Iceberg B-15
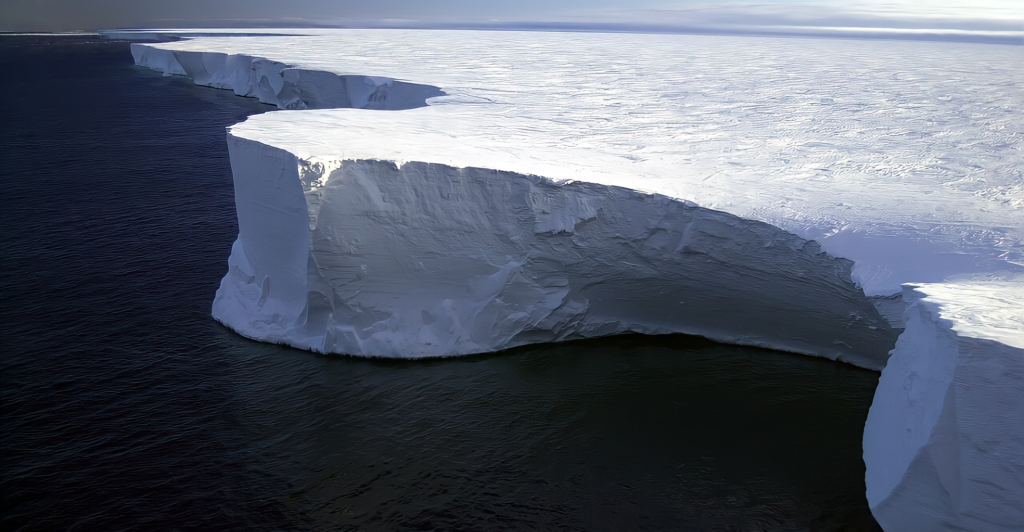

In 2000, Iceberg B-15, the most enormous recorded iceberg by area, calved from the Ross Ice Shelf. Measuring around 11,000 square kilometers, B-15 eventually broke into smaller pieces. Its presence near McMurdo Sound disrupted ocean currents and sea ice patterns, affecting local wildlife such as Adélie penguins and Weddell seals. This historical event provides insights into the potential ecological impacts of large icebergs.
Impact on Penguin Populations
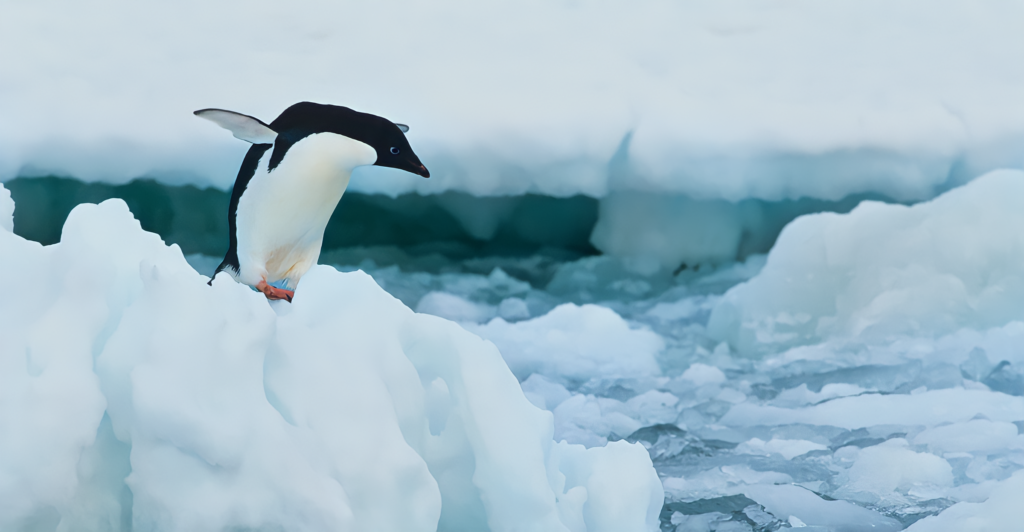

A23a grounds near South Georgia could obstruct access to feeding areas for penguin species like Gentoo, macaroni, and king penguins. Such blockages may force these birds to travel longer distances to find food, potentially leading to decreased breeding success and chick survival rates. Past events have shown that iceberg-induced disruptions can significantly affect penguin colonies.
Effects on Seal Communities
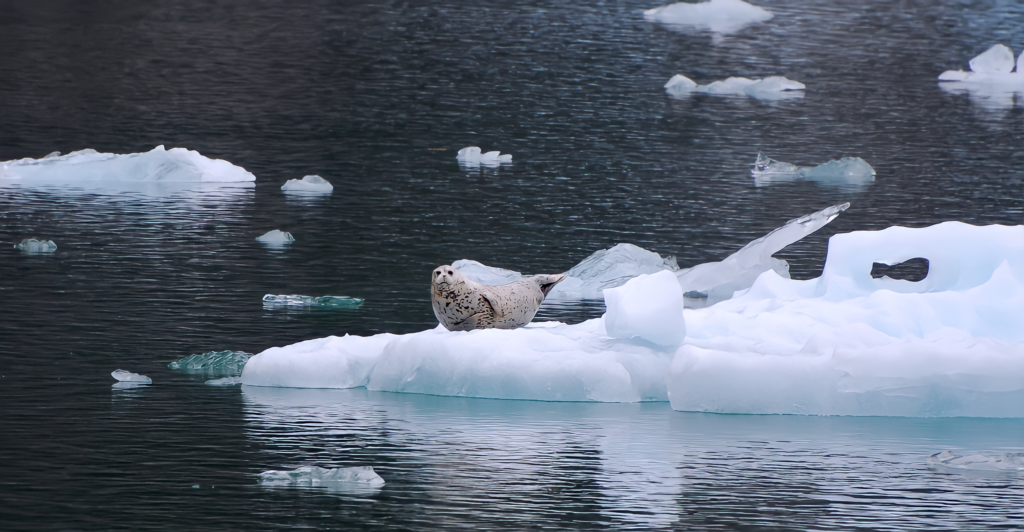

Seal species, including elephant and fur seals, rely on accessible beaches and abundant feeding grounds around South Georgia. A grounded iceberg could alter these habitats by changing prey availability and making certain areas inaccessible. This could increase competition for resources and impact seal pup survival rates. Monitoring these potential changes is crucial for understanding the broader ecological consequences.
Nutrient Enrichment from Melting Icebergs
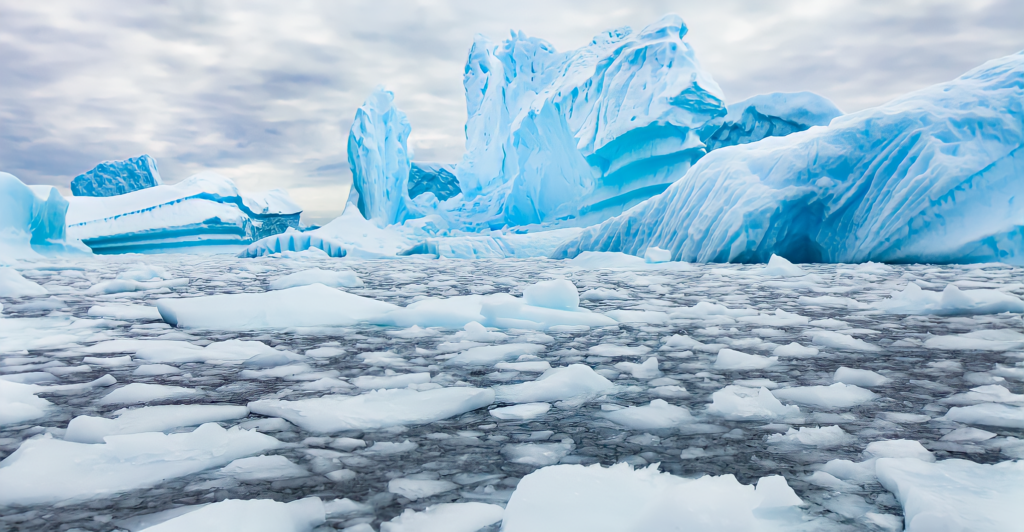

As icebergs melt, they release freshwater enriched with nutrients like iron into the surrounding ocean. This process can stimulate phytoplankton blooms, forming the base of the marine food web. While such enrichment can boost local productivity, the extent and duration of these effects depend on various factors, including the rate of melting and ocean currents.
Alteration of Oceanographic Conditions
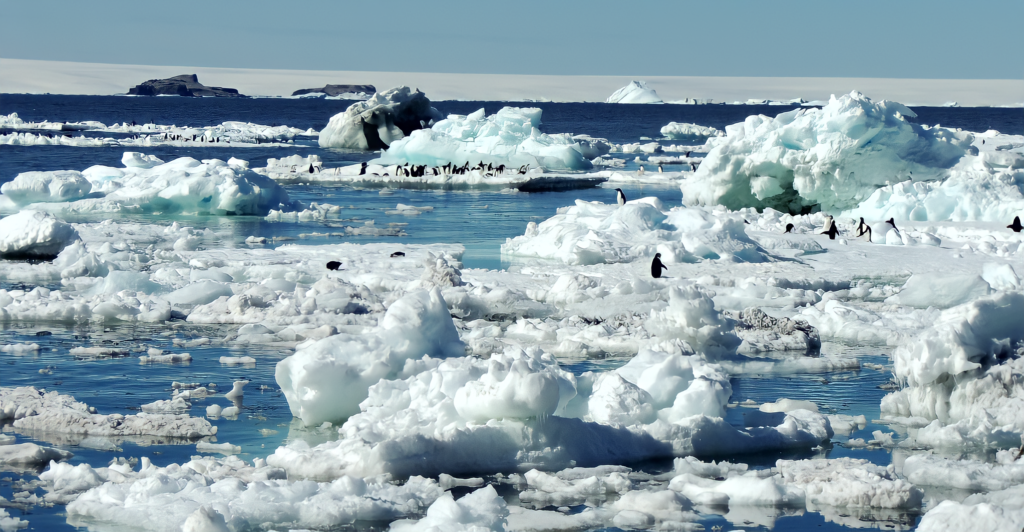

Introducing large volumes of freshwater from a melting iceberg can alter local oceanographic conditions, including salinity and temperature. These changes can affect the distribution and abundance of marine species, from microscopic plankton to larger predators. Understanding these dynamics is essential for predicting the ecological impacts of large icebergs like A23a.
Potential Benefits to Marine Ecosystems

While large icebergs can disrupt existing ecosystems, they may also create new habitats. Icebergs can provide surfaces for algae to grow and shelter various marine organisms as they melt. Additionally, the release of nutrients can enhance local productivity, supporting diverse marine life. These potential benefits highlight the complex role icebergs play in ocean ecosystems.
BBC.COM
Long-Term Ecological Implications
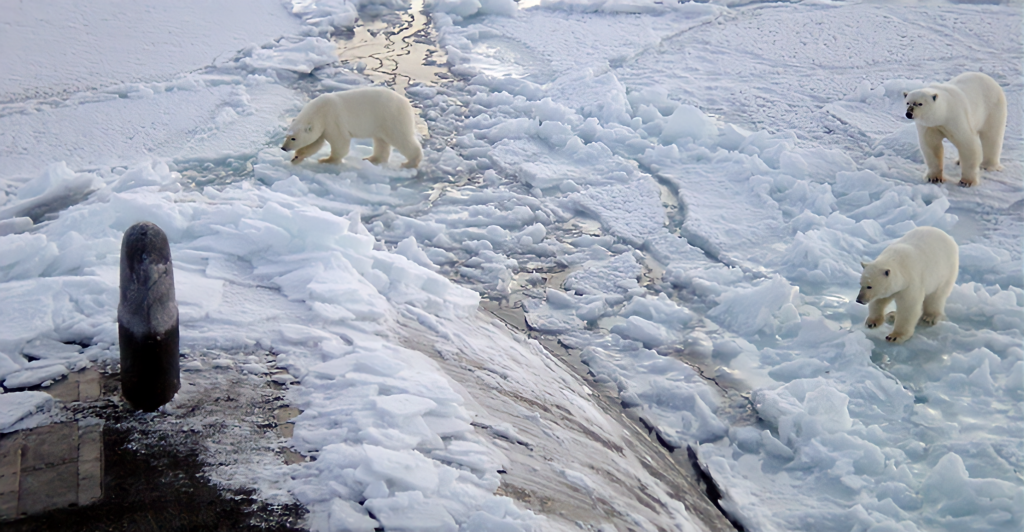

The long-term ecological implications of a considerable iceberg grounding near South Georgia are uncertain. Potential outcomes include shifts in species distributions, changes in predator-prey relationships, and alterations in nutrient cycling. Continuous monitoring and research are necessary to understand these impacts and inform conservation efforts.
The Role of Climate Change

Climate change, due to warming temperatures and melting ice shelves, contributes to the increased calving of large icebergs. The frequency of such events may rise, leading to more frequent ecological disturbances. Understanding the relationship between climate change and iceberg dynamics is crucial for predicting future impacts on marine ecosystems.
Monitoring and Research Efforts

Scientists monitor icebergs like A23a using satellite imagery, oceanographic measurements, and ecological surveys. These efforts aim to track iceberg movements, melting rates, and associated ecological impacts. Such research is vital for developing strategies to mitigate potential adverse effects on marine life and to enhance our understanding of polar ecosystems.
Balancing Risks and Benefits
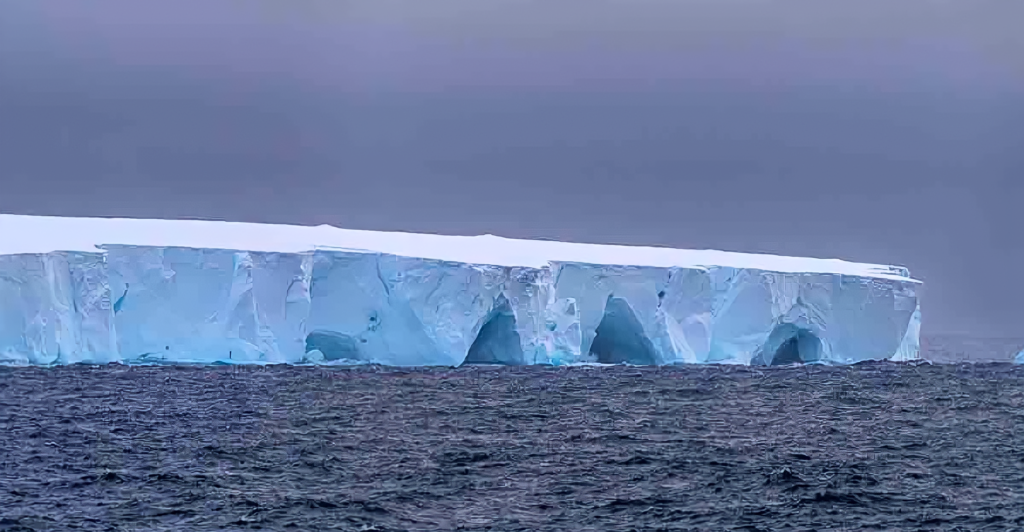

The potential collapse or grounding of the world’s largest iceberg, A23a, presents risks and opportunities for marine ecosystems. While there are concerns about habitat disruption and species displacement, there are also possibilities for nutrient enrichment and habitat creation. Ongoing research and monitoring are essential to navigate these complexities and to develop informed conservation strategies.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
California Is Breaking Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
“There Will Be Eruptions”: Concerns Mount as Yellowstone Supervolcano Activity Shifts
Philanthropist Promises To Cover $771.23M Annually After US Exit From Climate Accords
The War on Cows Is Over—And Green Extremists Have Lost
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







