
In the search for more sustainable farming practices, an unexpected resource is gaining attention—insect waste. Studies show that insect frass, a mix of excrement, uneaten feed, and shed exoskeletons, is packed with essential nutrients that can improve soil health. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, it provides an eco-friendly alternative that supports regenerative agriculture.
Boosting Soil Health

Research has found that adding mealworm frass to soil significantly increases carbon and nitrogen levels, enhancing fertility and promoting healthy plant growth. The results show that crops grown in frass-enriched soil yield at rates comparable to those using conventional fertilizers.
A Natural Fertilizer for the Future

As insect farming expands, frass has the potential to reshape modern agriculture. Its nutrient-rich composition makes it a cleaner, sustainable alternative to traditional manure, offering farmers a way to improve soil health without relying on synthetic fertilizers.
Eco-Friendly Farming

Unlike chemical-based options, frass also contributes to long-term soil vitality by enhancing microbial activity and organic matter. As the demand for eco-friendly farming solutions grows, insect frass could play a crucial role in building a more resilient and sustainable food system.
Rich In Carbon And Nitrogen

Researchers led by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS) found that frass can compete with fossil fuel-based fertilizers while being a cleaner alternative to traditional animal manure.
A Collaboration

The ARS team later collaborated with partners from the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture. They conducted a two-year field study on frass as an organic soil amendment. The results were quite remarkable.
Yellow Mealworm Frass
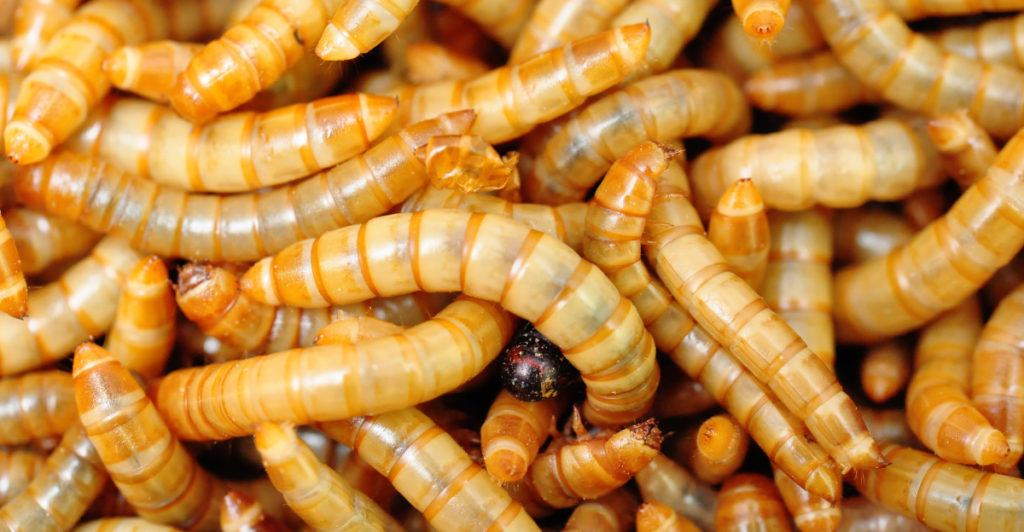

What stood out was yellow mealworm frass, which doubled the soil’s carbon content while tripling its nitrogen content. This was significantly higher than poultry litter and ammonium nitrate.
Similar Rates

Most notably, soil enriched with frass yielded crops at similar rates and maintained carbon dioxide emissions comparable to soils amended with poultry litter and ammonium nitrate.
An Alternative

“Insect frass substantially improved soil fertility which showed its ability to be used as an alternative to inorganic fertilizers,” Amanda Ashworth, a soil scientist at the ARS Poultry Production and Product Safety Research Unit in Fayetteville, Arkansas, said.
On The Rise

“This is important since insect farming is on the rise and circular agricultural systems (agricultural by-products that are recycled back into production systems) can be sustainable avenues for growing foods in the future.”
Growing Rapidly

Meticulous Research’s Global Edible Insects Market Forecast to 2030 reports that the insect farming industry is rapidly growing due to the rising demand for sustainable protein in animal feed. The market is expected to expand at an annual rate of 28%, reaching an estimated value of $8 billion by 2030.
Sustainable Practices

The agricultural industry is moving toward sustainable practices, and insect frass is gaining recognition as a valuable tool in regenerative farming. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, which can contribute to soil degradation and water contamination, insect frass provides a natural alternative that enhances soil health while reducing environmental impact.
A Promising Solution
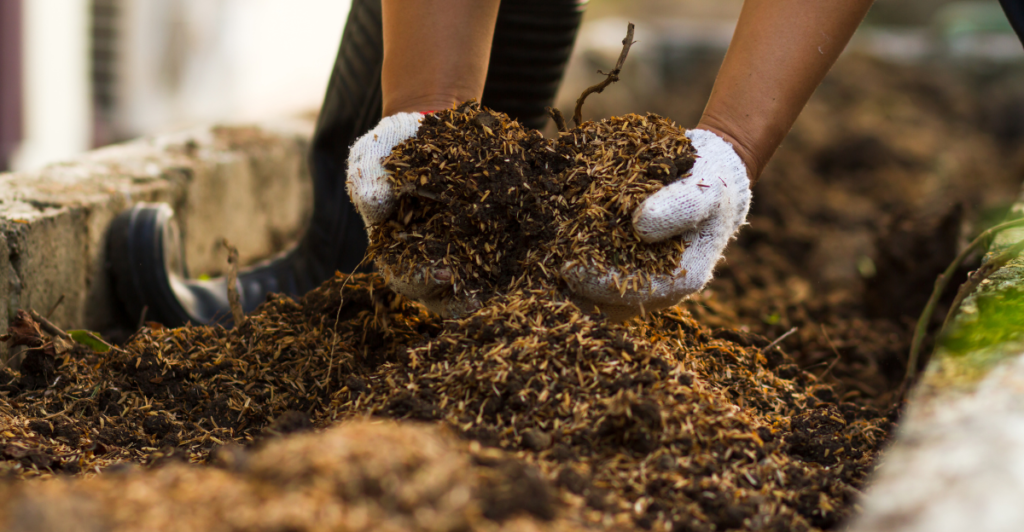

Its nutrient-rich composition makes it a promising solution for improving soil fertility without the harmful side effects of chemical-based fertilizers. Beyond supplying essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, insect frass actively supports soil biodiversity. It stimulates microbial activity, encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria and fungi that play a crucial role in soil structure and plant health.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
California Is Breaking Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
Philanthropist Promises To Cover $771.23M Annually After US Exit From Climate Accords
The War on Cows Is Over—And Green Extremists Have Lost
Lake Shasta’s Remarkable Comeback From Drought Captured in Stunning Images
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







