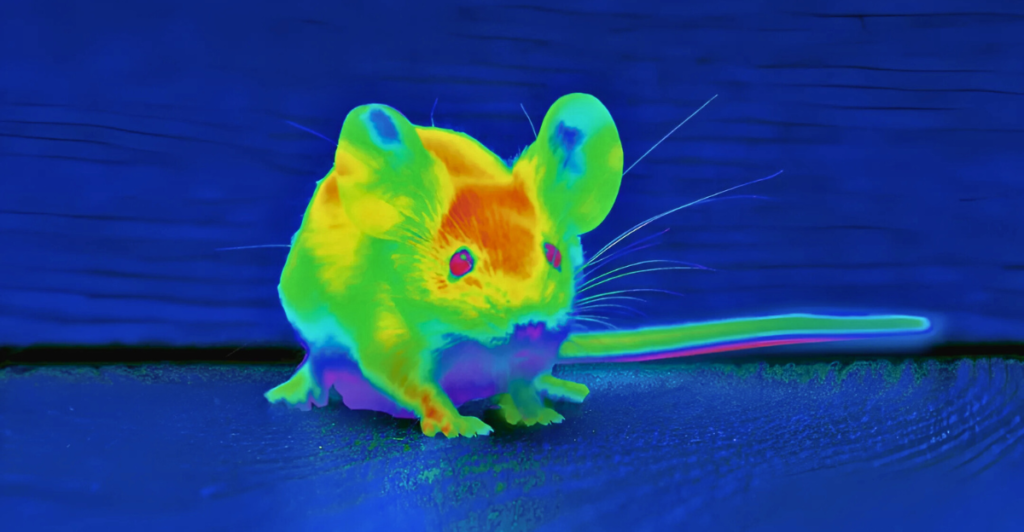
Ever wonder what heat looks like? While we squint in the dark, some creatures have heat detection senses. They see heat as light. Some animals have mastered this, giving them an edge when it comes to survival in the wild. It means they can hunt, hide and guide themselves in ways we can’t imagine.
1. Pit Vipers: The OG Heat Seekers
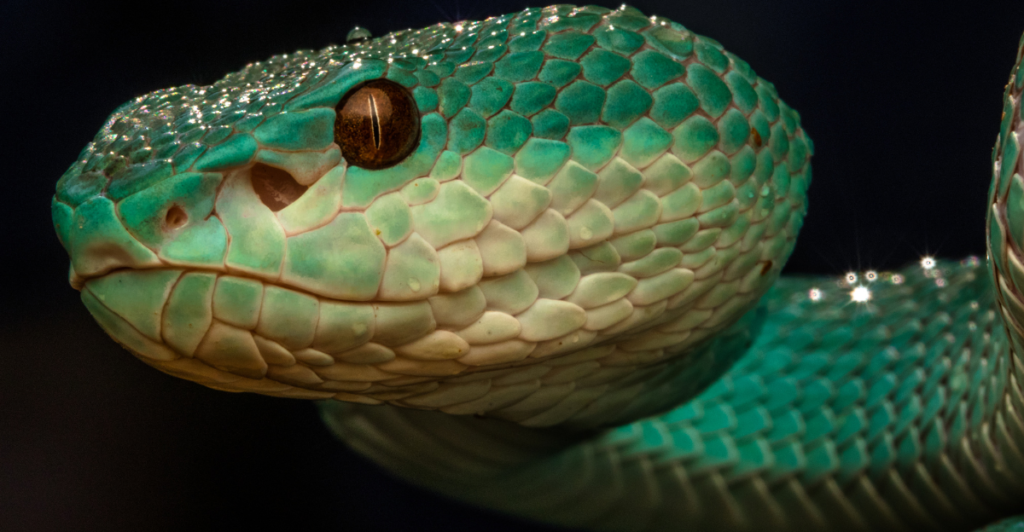

Imagine: a rattlesnake in pitch black darkness, approaching its prey with supernatural precision. The cold-blooded hunter has heat-sensing cavities between its eyes and nostrils that serve as a kind of thermal camera. It’s like having vision goggles. That’s the daily experience of a pit viper.
2. Bullfrogs: The Amphibian Heat Detectives
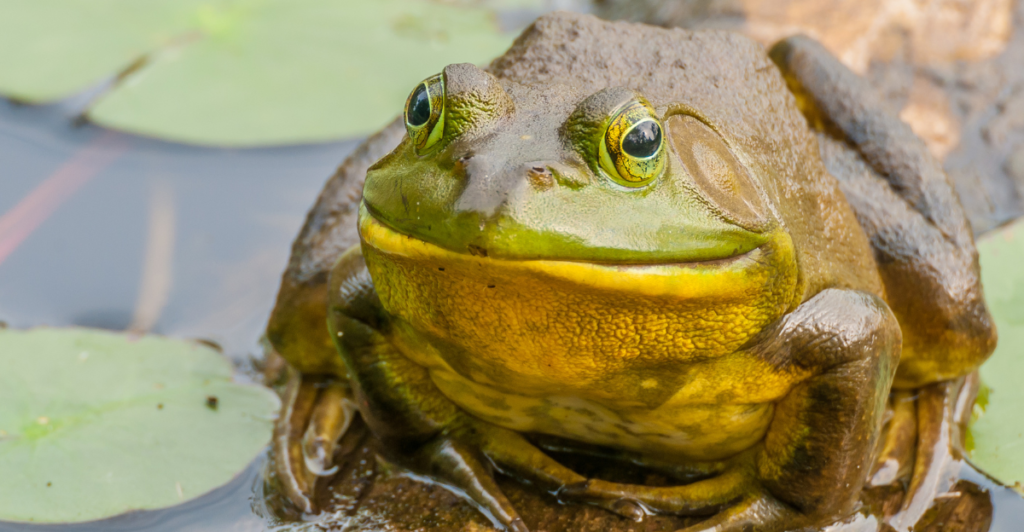

Bullfrogs don’t just dwell in ponds. Thanks to Cyp27c1, a supernatural enzyme, they can detect heat signals below and above water. They can detect thermal cues, helping them not only survive but also hunt.
3. Goldfish: The Unexpected Light Spectrum Champions
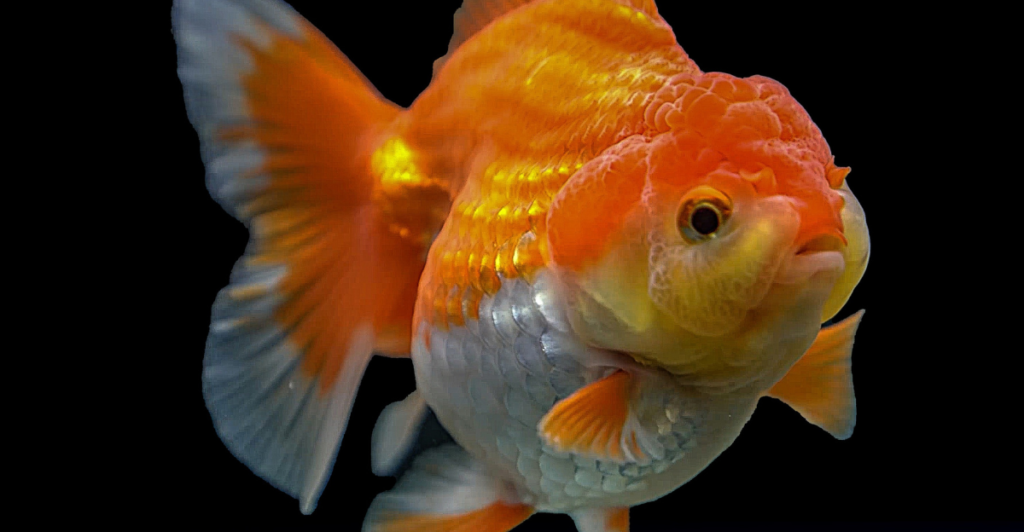

Next, who would have known Goldfish could see infrared and ultraviolet light? Thanks to adapted cone cells, they can easily move through murky waters, sense predators, and find food with ultimate precision. While humans fumble around in dim light, Goldfish operate like underwater secret agents, effortlessly perceiving a world we can’t.
4. Mosquitoes: The Bloodsucking Heat Missiles
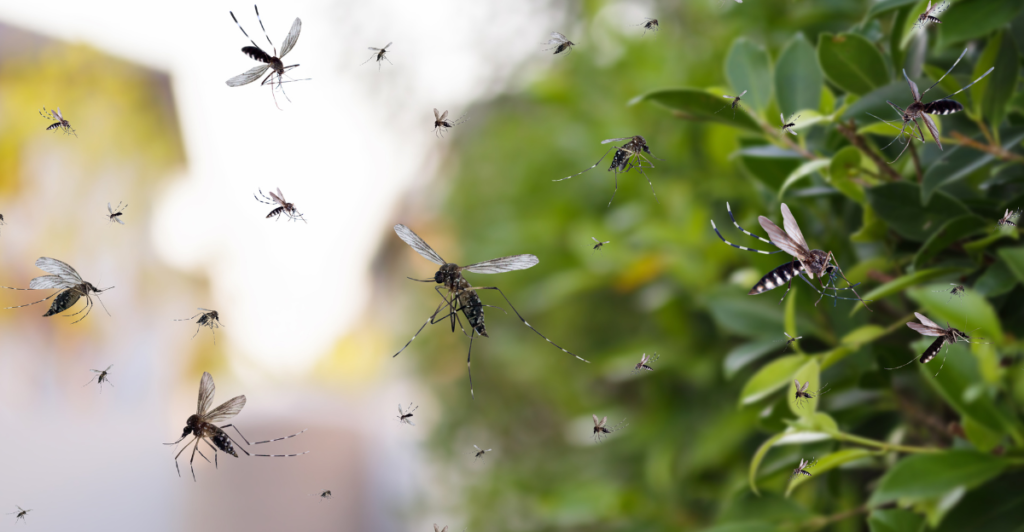

Mosquitoes, for all their irritations, are infrared spotting machines. They detect carbon dioxide emissions and body heat accross very long distances. They make our best heat tracking systems look like toys in comparison.
5. Vampire Bats: Thermal Hunters
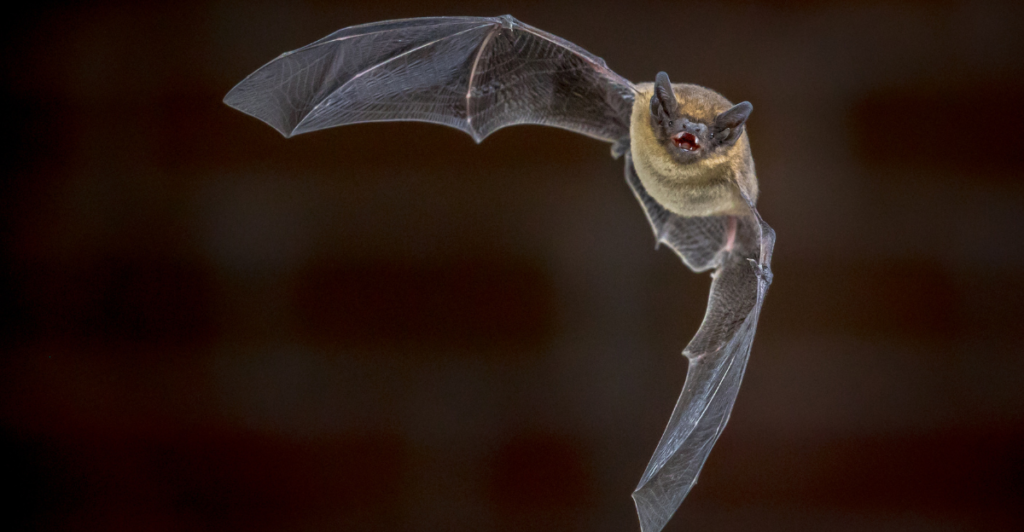

Vampire bats have infrared sensors that allow them to locate their warm-blooded prey. They have tiny nerve endings in their nostrils that pick up infrared radiation. This ability enables them to locate warm-blooded prey with the utmost precision.
Why Warm-Blooded Animals Can’t See Heat

Warm-blooded animals can’t detect infrared because their own temperature creates too much “noise.” It’s as if you tried to listen to whispering at a rock concert—you can’t.
The Science Behind the Magic
Some creatures use particular proteins, others rely on special enzymes. For instance, frogs use vitamin A-linked mechanisms to turn heat into perception while snakes have protein channels in their pit organs.
Infrared vs. Night Vision: Know the Difference
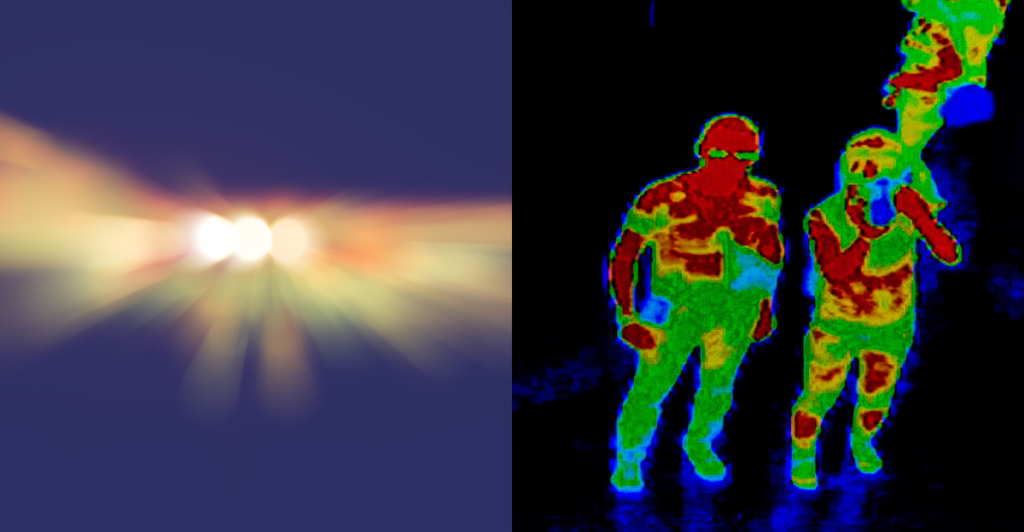
Did you know? There’s a difference between infrared vision and night vision: infrared vision detects heat, while night vision simply enhances exisiting light. Animals with infrared abilities can perceive warm objects in pitch darkness; a special ability that puts our technology to shame.
From Nature to Innovation
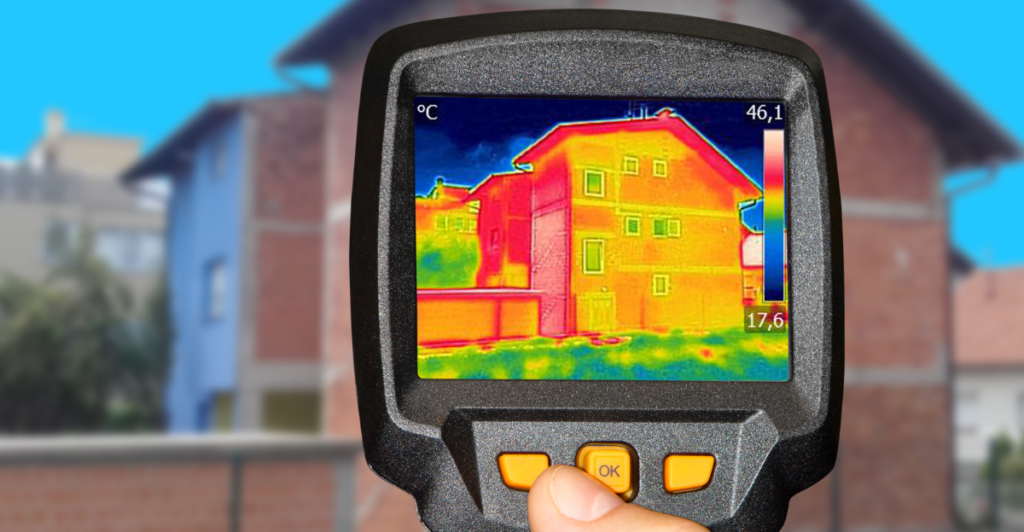

Scientists are fascinated by these animals’ powerful abilities. They are studying them, and as a result, creating revolutionary technologies like advanced thermal imaging cameras. Who would have imagined vampire bats and mosquitoes could inspire modern military and medical tech?
Survival of the Warmest

Infrared vision isn’t just a cool ability for these animals; it can mean life or death. From navigating murky waters to detecting prey or predators in tough environments, evolution has equipped them against the dangers of their world.
Not All Heat Detection is “Vision”

Here’s a brain-twister: not all animals that can detect heat can actually “see” it. Snakes, for instance, detect heat with their organs, not their eyes. Biology is fascinating, isn’t it?
Nature’s Thermal Superstars

From bullfrogs picking up thermal signals to goldfish seeing beyond our own perception, these creatures remind us that nature far exceeds our limited sensory world. Their extraordinary abilities remind us that, when we look at the bigger picture, we’re just small fish in a big pond.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
12 Animals With Paradigm-Shifting Impacts On Wildlife Conservation
13 Incredible Things Dogs Can Smell That Humans Never Will
12 Fascinating Horses That Are Anything But Ordinary
Hurricane-Like Bomb Cyclone Set to Impact These 8 States
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







