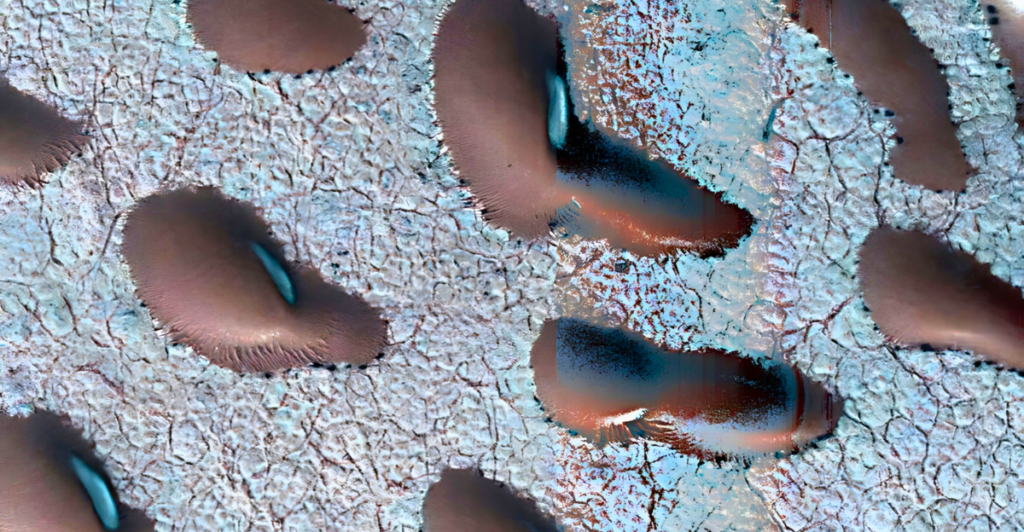

A recent discovery of unusual formations on Mars has sparked excitement among scientists and space enthusiasts alike. Satellite images, taken using NASA’s specialized cameras in 2022, revealed giant kidney bean-like structures, which could provide important insights into the planet’s history and potential for life.
The Discovery of Kidney Beans
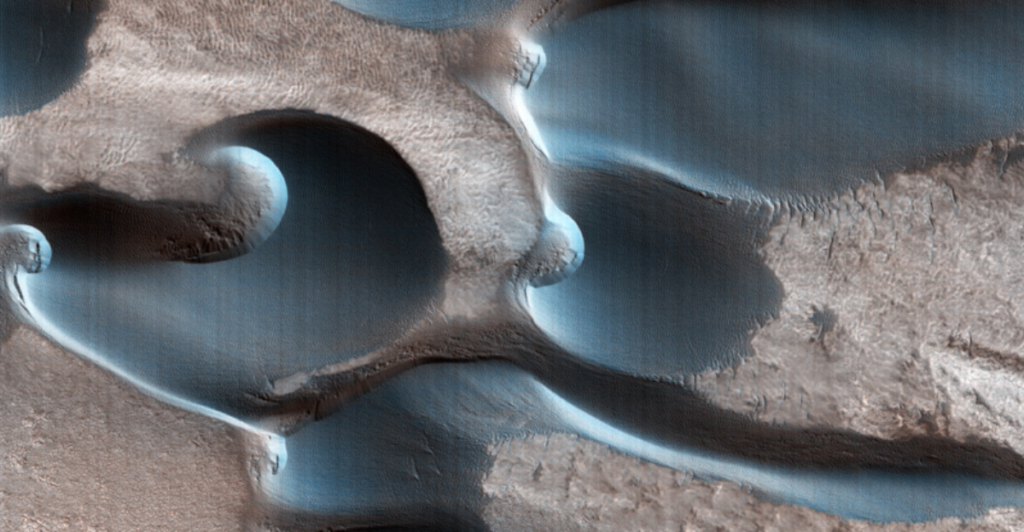
The images were taken with the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera in September 2022 onboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The kidney bean structures are frozen sand dunes in the planet’s northern hemisphere. The discovery could answer whether or not conditions on Mars could have previously sustained life.
What are Giant Kidney Beans?
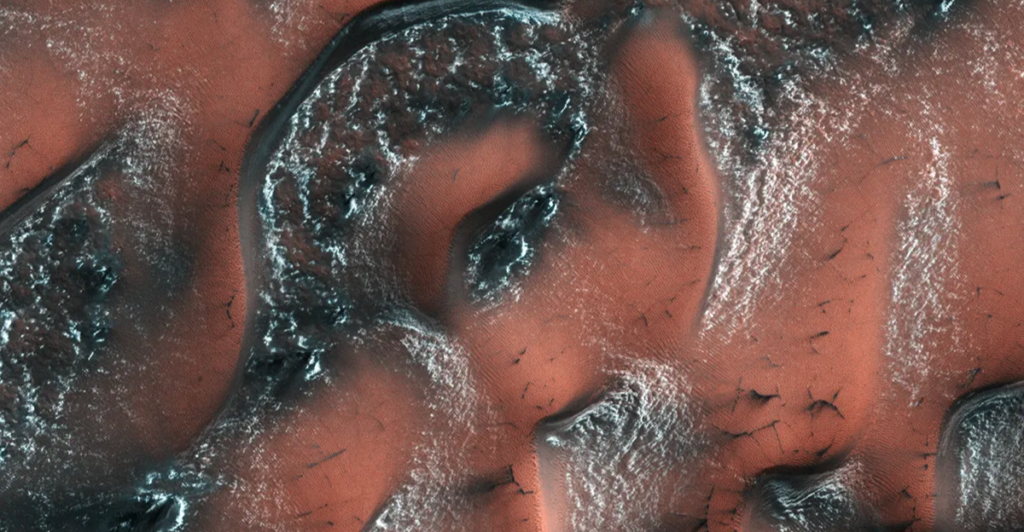
The dunes are characterized by their elongated, curved shapes and smooth surfaces, resembling terrestrial kidney beans. Scientists suggest they may result from geological processes involving water, ice, or biological activity. Understanding their composition is crucial for determining their significance.
Mars Dunes vs Earth Dunes
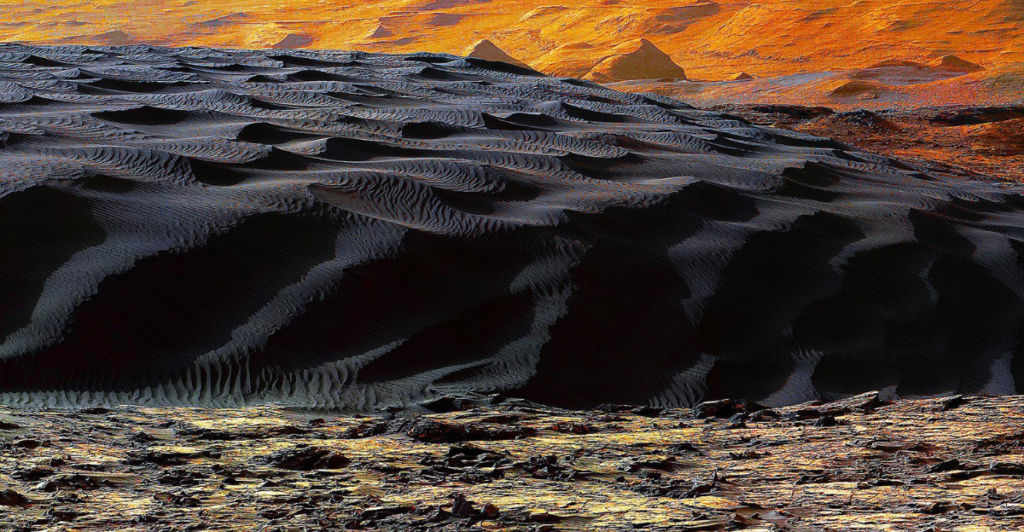

Like dunes found on Earth, Mars’ dunes move as the wind blows grains of sand from one side to the other. What makes Mars’ dunes different is that they do not appear to move. Earth’s dunes are constantly changing, but from the images captured on the HiRISE camera, Mars’s dunes are completely motionless because they are coated in carbon dioxide frost.
The Significance of Water on Mars
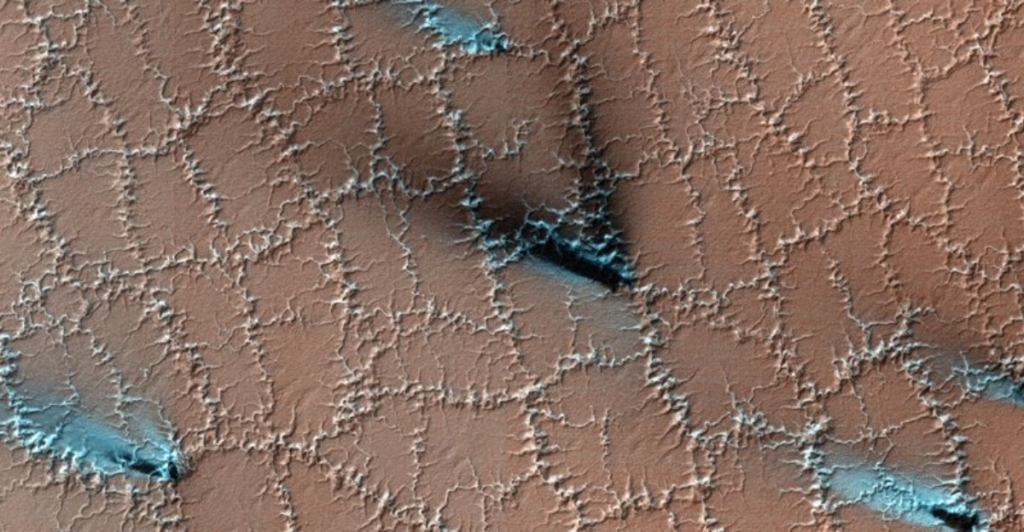

The dunes could add insight into researchers’ understanding of how carbon dioxide frosts occur on the planet. Scientists discovered that Mars’ winter frost stops the movement of sand grains, freezing the dunes in place until the Martian weather changes to spring. This is when dunes have been seen moving again. The presence of this frost indicates the significance of water on the planet.
Weather on Mars
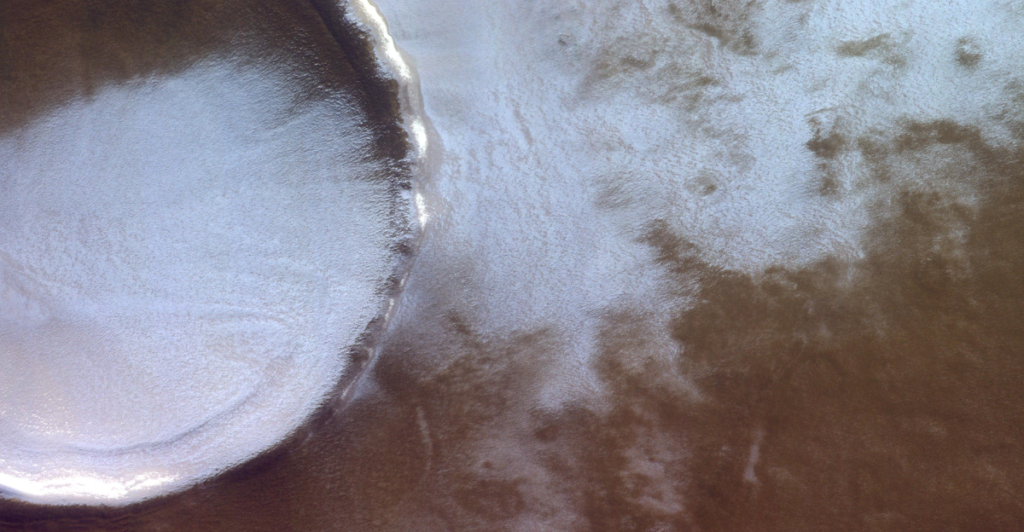

NASA has observed that Mars’ winter months can experience nighttime temperatures of -190 degrees Fahrenheit, creating ideal conditions for snow and frost. Mars has two snow forms – water ice and frozen carbon dioxide (or dry ice). Frost is made from water and carbon dioxide ice and stops the wind from moving sand grains. Studying this phenomenon can help better understand the planet’s climate conditions.
Geological Implications
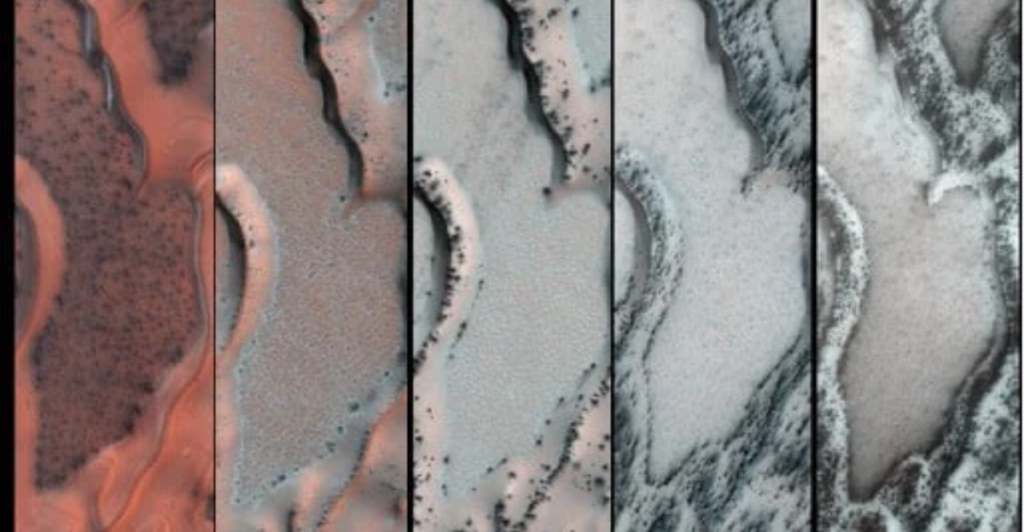

NASA indicates that Mars’ northern hemisphere is different every spring. As the sun shines on the planet, the ice turns from a solid to a gas, which accounts for the makeup of Mars’ atmosphere (carbon dioxide). This continual change in the springtime leads to ice sublimating faster or slower, which in turn controls other phenomena on the planet’s surface.
Potential Signs of Life
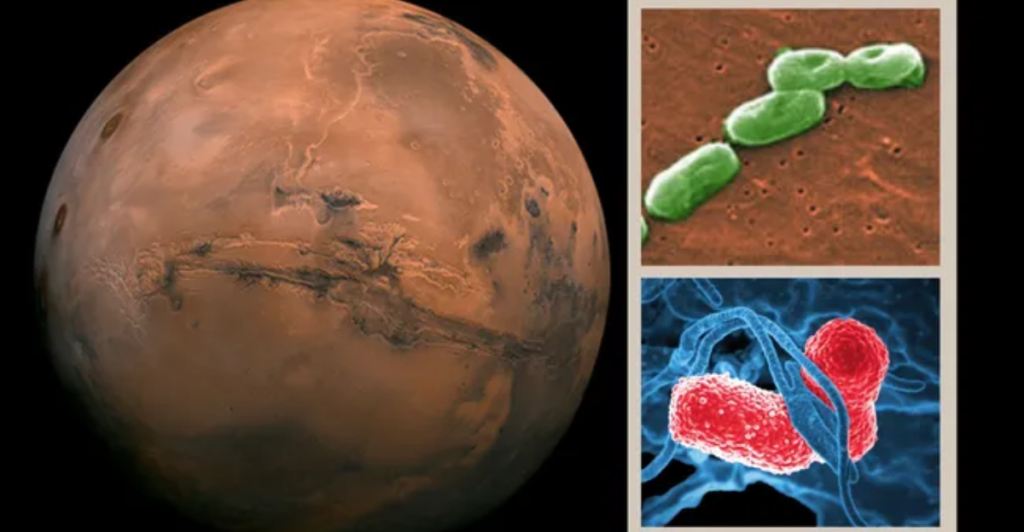
Through this discovery, scientists believe that frozen dunes could provide more insight into whether or not microbes could survive beneath the frozen water on the planet’s surface. Additionally, scientists have suggested that the planet’s sunlight might be enough for photosynthesis in shallow pools of meltwater beneath the ice. However, it must be noted that there is no evidence of previous or potential animal life on the planet.
Mars Magnetic Field
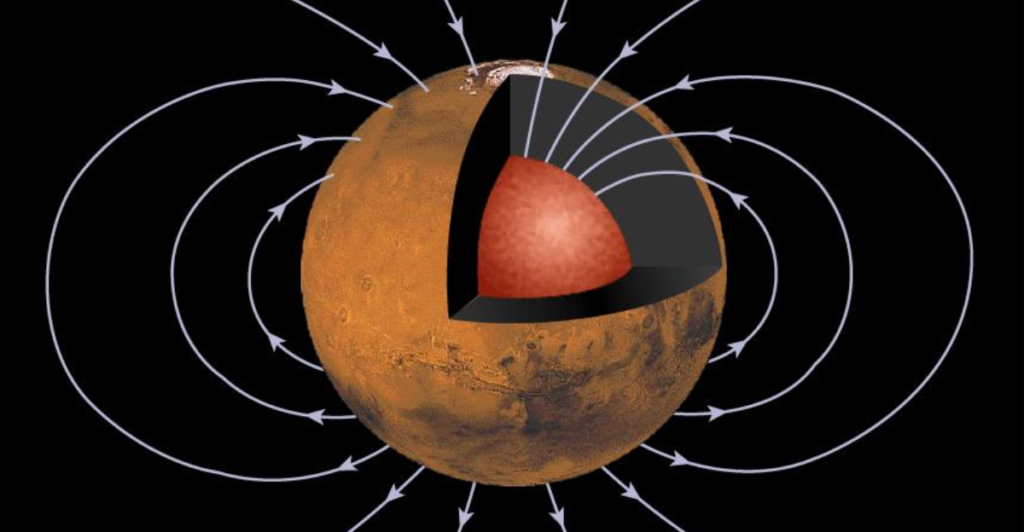
Researchers at Harvard’s Paleomagnetics Lab published a study that suggests that Mars’ protective magnetic field could have supported life millions of years ago. The study outlined how researchers used simulation and computer modeling to estimate the age of Mars’ global magnetic field, produced by convection in the planet’s iron core (otherwise known as its “dynamo”).
The Importance of the Dynamo
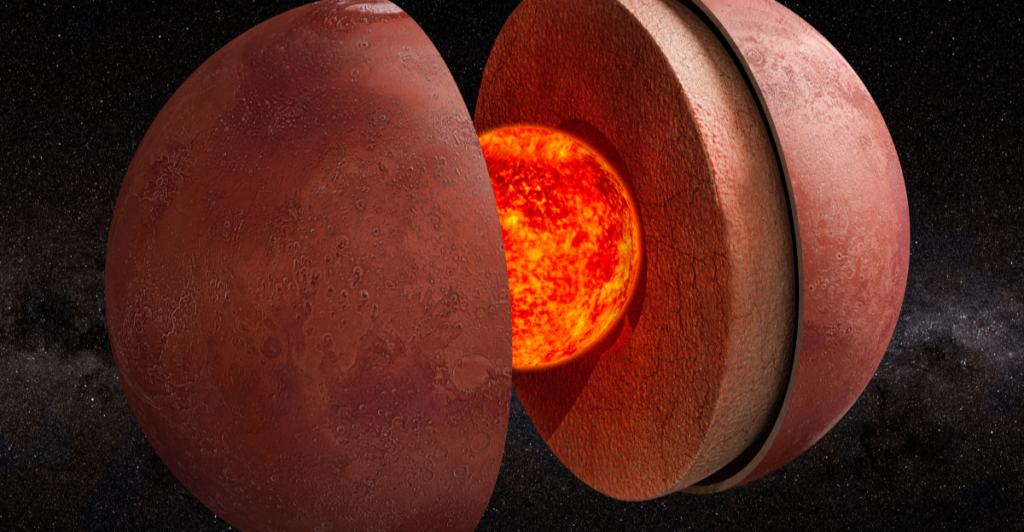
The study indicated that Mars’ dynamo could have survived until roughly 3.9 billion years ago and could deflect harmful cosmic rays. Previously, weaker magnetic fields in Mars’ basins, which were explored by NASA, indicate that the planet’s dynamo had gone away some 4.1 billion years ago; however, this study revealed that craters were more likely formed while the dynamo was experiencing a polarity reversal.
Polarity Reversal
Polarity reversal is the process by which the north and south poles switch places. This even happens on Earth every hundred thousand years. Without the magnetic field on the planet, Mars lost the ability to ward off solar wind, which then destroyed its atmosphere and eroded all signs of water, making life unsustainable.
Other Significant Martian Discoveries

Last year, NASA discovered the presence of sulfur stones on Mars. The Curiosity Mars rover captured the stones in the Gediz Vallis channel when it accidentally crushed some rocks open. Curiosity’s Alpha Particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) found that the crystalline material inside the rock was elemental sulfur. It is not yet clear how these stones formed on the planet.
Our Understanding of Mars

Scientists, space enthusiasts, and researchers alike have long been looking for signs of life on other planets, especially Mars. But with this new discovery that frozen water can be found in the planet’s northern hemisphere and that photosynthesis might be possible within the kidney bean-like structures, researchers will be able to study the planet’s history as well as its future.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
California Is Breaking Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
There Will Be Eruptions”: Concerns Mount as Yellowstone Supervolcano Activity Shifts
Deepest Hole On Earth Permanently Sealed After 2 Billion Year Old Discovery
Climate Change Overestimated? New Data Shows Oceans Are Cooling The Planet Faster Than Predicted
References:
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
This article first appeared here
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







