
Recent research suggests that oceans may absorb heat faster than previously thought, potentially moderating the effects of climate change. This discovery comes from advanced monitoring systems that track ocean temperatures globally. Scientists emphasize the importance of understanding these dynamics to create more accurate climate models. While this doesn’t negate concerns about global warming, it highlights the oceans’ critical role in regulating Earth’s climate and underscores the need for continued study.
The Science Behind Ocean Cooling

Oceans act as Earth’s most significant heat sink, absorbing over 90% of the heat trapped by greenhouse gases. New data indicates that this heat absorption process may be more efficient than once believed. Ocean currents and deep water layers distribute heat, preventing surface temperatures from rising as quickly. Researchers caution, however, that while oceans can delay warming, they don’t eliminate the long-term risks of climate change.
Understanding Heat Absorption Rates

The rate at which oceans absorb heat depends on factors like salinity, depth, and current systems. Recent findings show that deep ocean layers take up more heat than surface layers, challenging older models. This redistribution of heat helps stabilize atmospheric temperatures temporarily but could have long-term implications for marine ecosystems. Understanding these rates is crucial for refining climate predictions and preparing for future impacts.
Regional Variations in Ocean Cooling

Not all oceans absorb heat at the same rate. The Atlantic Ocean, for example, exhibits stronger heat absorption due to its unique current system. Meanwhile, the Pacific and Indian Oceans show slower rates of heat uptake. Factors like wind patterns, salinity, and geological features drive these regional differences. Mapping these variations helps scientists predict localized climate effects and plan for region-specific environmental challenges.
Impacts on Marine Life

The increased heat absorption by oceans affects marine ecosystems. Warmer waters can disrupt habitats, alter migration patterns, and impact breeding cycles for aquatic species. However, the heat distribution to deeper layers might temporarily relieve surface ecosystems. Scientists stress the importance of monitoring marine biodiversity as a critical indicator of how these changes impact global ecological balance.
Implications for Weather Patterns

Ocean heat absorption directly influences weather systems, from hurricanes to monsoons. Cooler surface temperatures in some regions could lead to less intense storms while warming in others might intensify weather events. These changes are already being observed in shifting wind patterns and precipitation rates. Understanding the interplay between ocean temperatures and weather systems is vital for improving forecasting and disaster preparedness.
How Data Was Collected
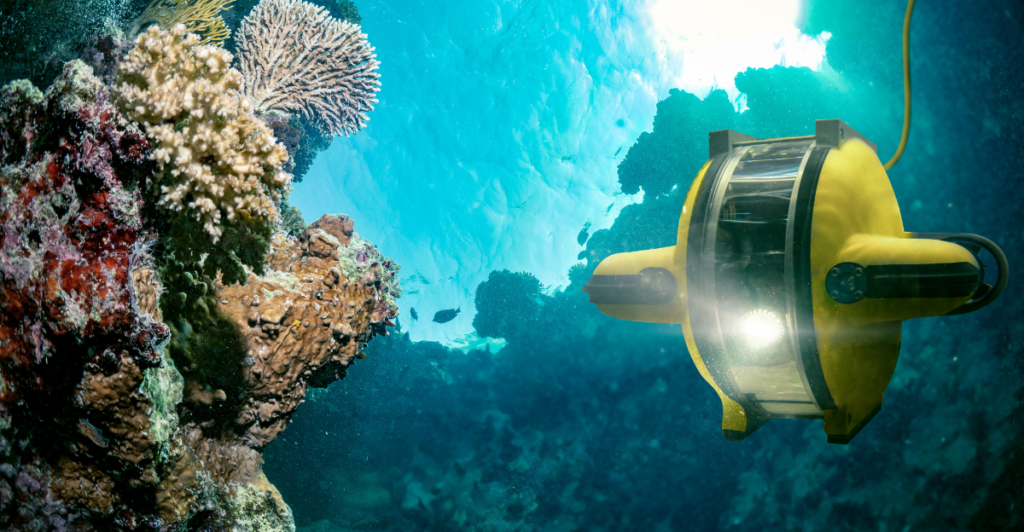

Technological advances, like underwater robots and satellite sensors, have revolutionized how scientists measure ocean temperatures. These tools provide real-time data from previously inaccessible depths. By analyzing this data, researchers can track heat distribution patterns and better understand the ocean’s role in climate regulation. This cutting-edge technology represents a significant step forward in climate science and monitoring.
Balancing Optimism and Caution
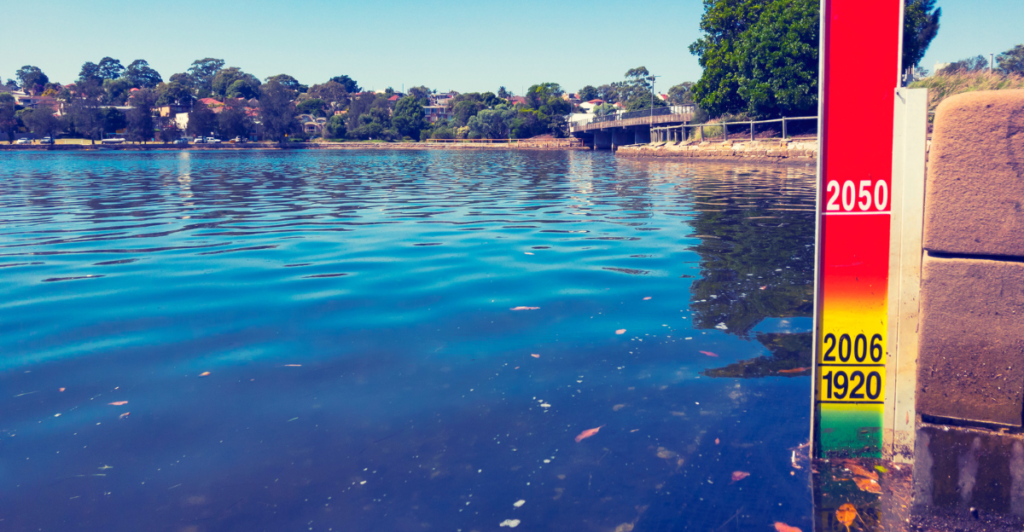

While the data suggests that oceans mitigate warming effects, scientists urge caution. This cooling effect is not unlimited and could mask the severity of climate change in the short term. Relying solely on oceans to absorb excess heat could lead to unforeseen consequences, such as ocean acidification and rising sea levels. Balanced perspectives are essential to avoid complacency and encourage proactive environmental policies.
Historical Context of Ocean Studies

Oceanography has evolved significantly over the past century. Early studies relied on rudimentary tools, providing limited insights into ocean temperatures and currents. Today, advanced models and data collection techniques offer a clearer picture of how oceans interact with the atmosphere. This historical progression underscores the importance of continued research and investment in understanding Earth’s most vital climate regulator.
The Role of Ocean Currents

Ocean currents play a crucial role in heat distribution. The Gulf Stream, for instance, transports warm water from the tropics to the North Atlantic, influencing weather patterns in Europe and North America. Recent data highlights how these currents help redistribute heat, balancing surface and deep ocean temperatures. Monitoring these systems is essential for predicting potential disruptions caused by climate change and their global implications.
Challenges in Climate Modeling

Incorporating ocean cooling data into climate models presents challenges. Oceans are vast and complex, with numerous variables affecting heat absorption and distribution. While new data improves model accuracy, uncertainties remain. Scientists continue refining their methods to ensure predictions reflect the latest understanding of ocean dynamics, emphasizing the importance of flexibility in addressing climate-related issues.
The Future of Climate Research

This new understanding of ocean cooling opens doors for further exploration. Future studies aim to investigate how long oceans can sustain their heat absorption capacity and the potential tipping points. Collaboration between nations, increased funding, and technological advancements will be critical in addressing these questions and preparing for future climate scenarios.
Why Public Awareness Matters

Raising awareness about ocean cooling is essential for fostering informed discussions about climate change. Understanding the complexities of ocean heat absorption can help people appreciate the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems. Public support for scientific research and environmental policies can drive meaningful action. By sharing accurate, balanced information, we can inspire collective efforts to address global challenges and protect our planet for future generations.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
California Is Splitting Apart: A Fault Line Is Forming Faster Than Anyone Predicted
12 Hidden Gem Destinations to Explore in 2025 – Every Nature Lover’s Dream
12 Edible Bugs That Could Help You Survive in Nature
11 Underrated Parks to Explore in the United States – A Nature Lover’s Dream
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







