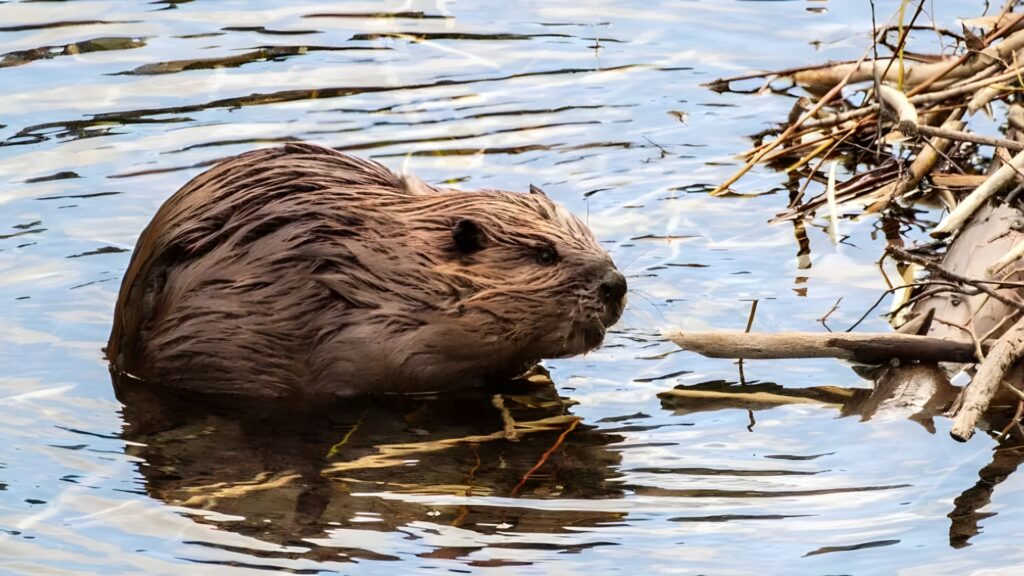

In boreal forests, wolves and beavers share a complex predator-prey relationship. Beavers are known as “ecosystem engineers,” shaping wetlands through their dam-building activities. Wolves, on the other hand, are apex predators with a diverse diet, now observed targeting beavers near ponds. This unique behavior has been noted in areas like Minnesota’s Voyageurs National Park, where wolves capitalize on the beavers’ predictable movements between land and water. These interactions reveal intricate ecological connections and showcase the delicate balance within these ecosystems.
Wolves Ambush Hunting Strategy
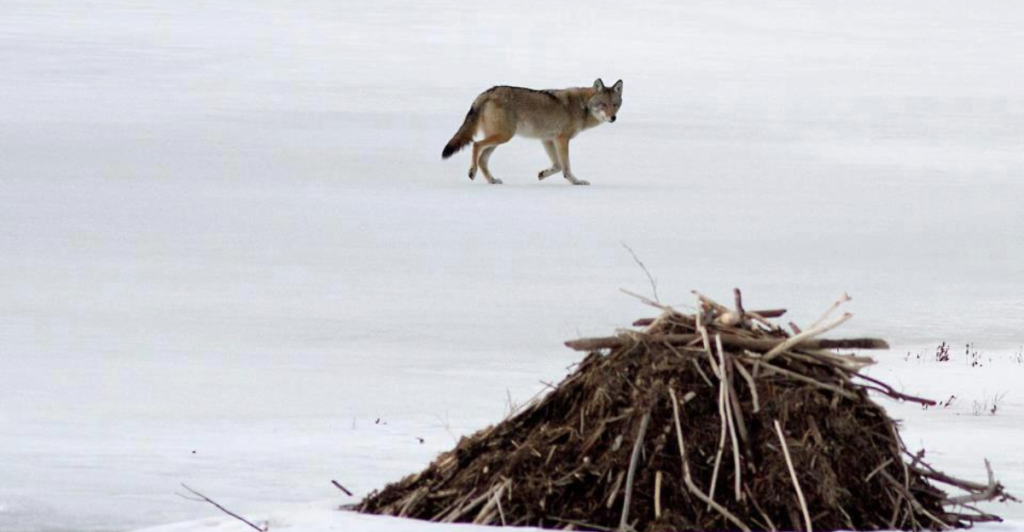

Wolves have adapted a unique hunting tactic when targeting beavers: ambush predation. Instead of hunting in packs, they often act alone, strategically positioning themselves near active beaver lodges or trails. By remaining motionless and downwind, wolves minimize the chance of detection. This approach takes advantage of beavers’ predictable foraging behavior. Ambush predation demonstrates wolves’ flexibility and intelligence in hunting methods, showcasing how they can tailor their strategies to prey types and environmental conditions, ensuring higher success rates in securing food.
Beavers’ Foraging Behavior and Vulnerability
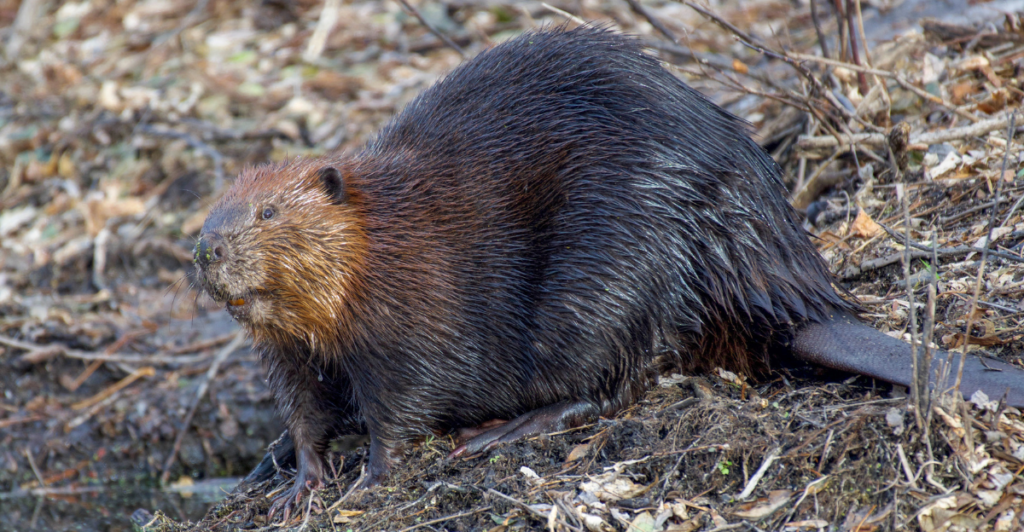

Beavers are central place foragers, meaning they rarely stray far from their water-based homes. Their predictable movements between aquatic safety and terrestrial foraging areas make them ideal targets for predators. Wolves exploit this behavior by waiting along well-worn beaver trails. While beavers rely on their environment for protection, their need to venture onto land to gather food and building materials exposes them to greater risk. This vulnerability highlights how environmental adaptations can sometimes create unforeseen challenges for prey species.
Sensory Limitations of Beavers
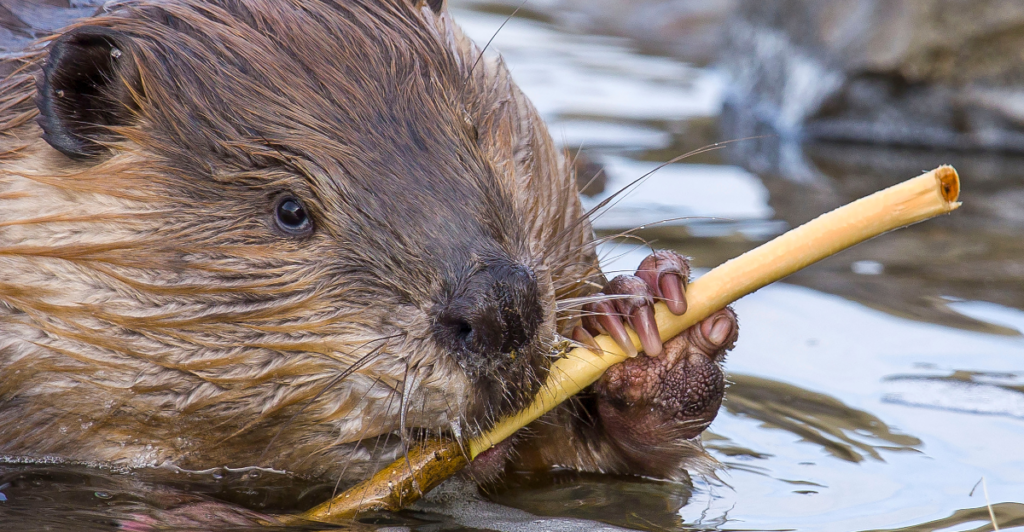

Despite their impressive engineering abilities, beavers have sensory limitations that make them susceptible to predation. Their vision and hearing are relatively weak compared to their sense of smell. Wolves exploit these weaknesses by approaching silently from downwind, staying undetected until it’s too late for the beaver to react. These sensory gaps, combined with their predictable behavior patterns, leave beavers at a significant disadvantage in predator encounters, particularly when they are far from the safety of their ponds and lodges.
Ecological Impact of Wolf Predation on Beavers
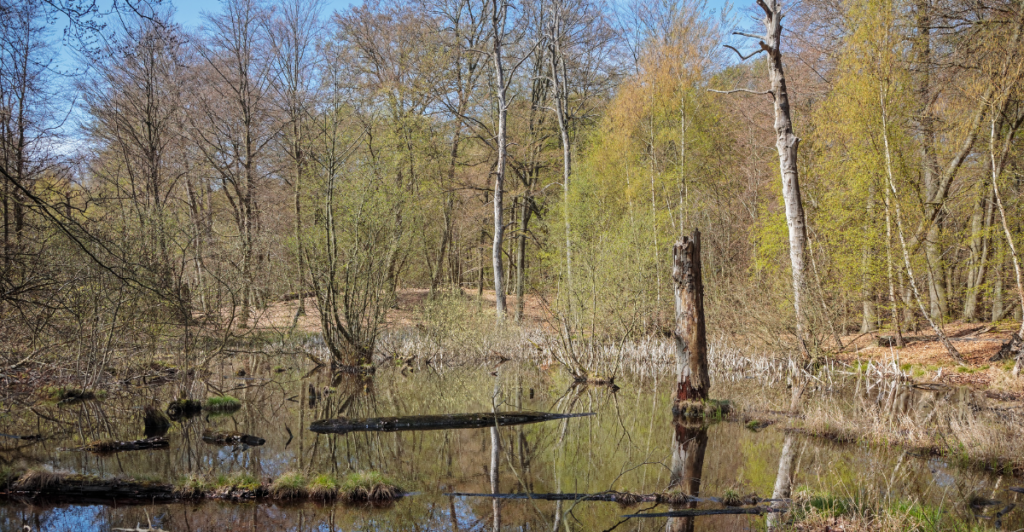

When wolves prey on beavers, the effects ripple through ecosystems. Beavers are responsible for creating wetlands by building dams, which serve as habitats for various species and play a role in water management. If wolves cause beaver populations to decline or abandon ponds, wetlands may dry up, impacting biodiversity and hydrology. This dynamic underscores the cascading effects predators can have on ecosystems, demonstrating the interconnectedness of species and the importance of maintaining balance within natural habitats for ecological stability.
Evolutionary Pressures and Behavioral Adaptations
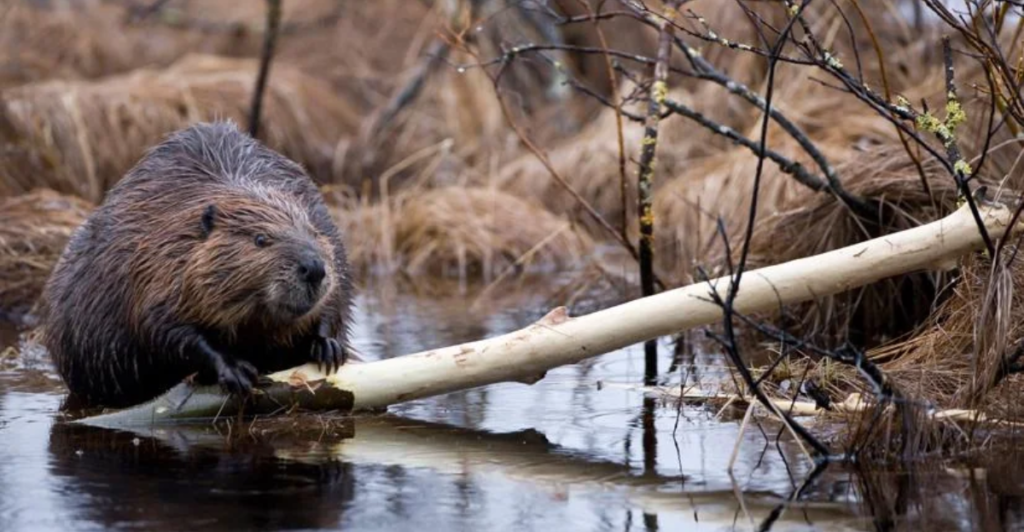

Predation by wolves imposes evolutionary pressures on beaver populations. Beavers may develop new behavioral strategies to minimize risk, such as altering their foraging times or staying closer to water. These changes can influence not only individual survival but also broader population dynamics. Meanwhile, wolves refine their hunting techniques in response, showcasing the ongoing arms race between predator and prey. This interplay highlights the adaptability of both species, contributing to the ever-changing nature of their ecological relationship and survival strategies.
Research Methodologies: Trail Cameras and Hair Snares
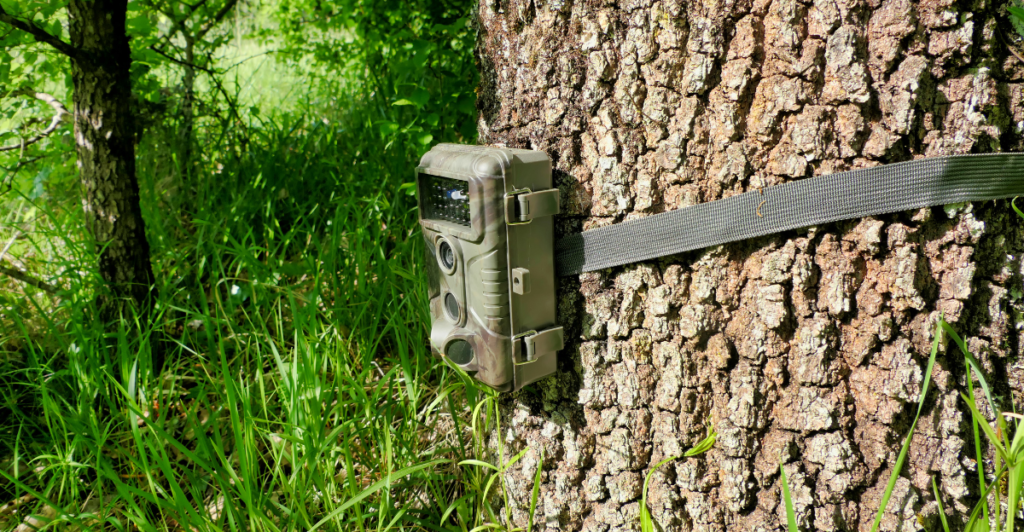

Studying wolves’ predation on beavers involves innovative research techniques like trail cameras and hair snares. Trail cameras provide visual evidence of wolves’ hunting behavior, capturing interactions in real-time without human interference. Hair snares collect fur samples for genetic and stress analysis, offering insights into the physiological impacts on both predator and prey. These tools enable researchers to observe the intricate dynamics between wolves and beavers, shedding light on their interactions and contributing to a deeper understanding of ecosystem processes.
Case Study: Voyageurs Wolf Project
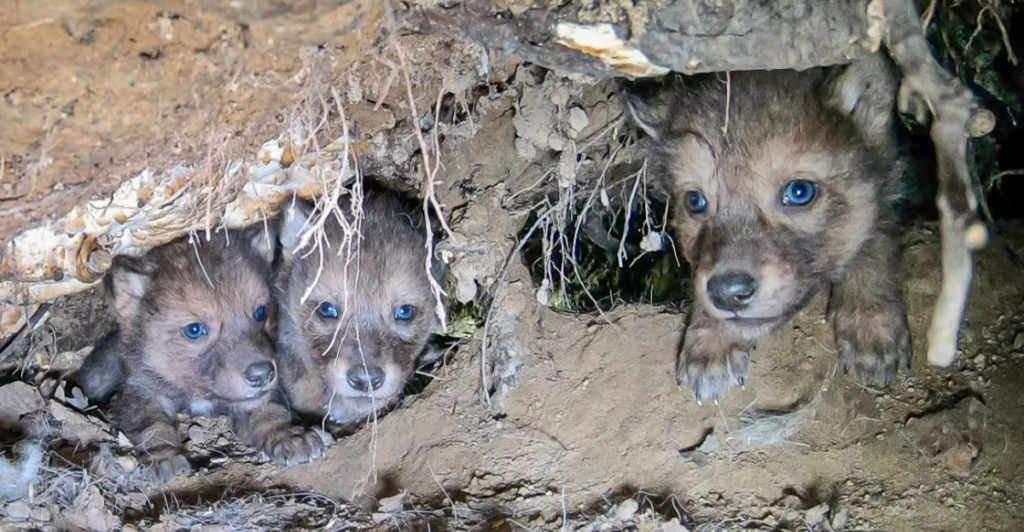

The Voyageurs Wolf Project has provided groundbreaking insights into wolf-beaver dynamics. By tracking wolves in Minnesota’s boreal forests, researchers documented how wolves ambush beavers, offering valuable data on their hunting strategies and success rates. Their findings reveal the significant role beavers play in wolf diets during warmer months. Additionally, the project highlights how these interactions influence wetland ecosystems. This research underscores the importance of studying predator-prey relationships to understand their implications for conservation and ecological balance in natural habitats better.
Implications for Forest Composition

Wolf predation on beavers has indirect effects on forest composition. Beavers play a pivotal role in shaping forests by selectively cutting trees for food and construction. When wolves target beavers, it reduces beaver activity in certain areas, allowing previously overharvested tree species to recover. Conversely, other vegetation types may flourish unchecked. These changes in vegetation dynamics can alter forest ecosystems, influencing biodiversity and long-term ecological trajectories. This indirect relationship demonstrates how predator-prey interactions extend beyond immediate survival to affect entire landscapes.
Broader Ecosystem Effects
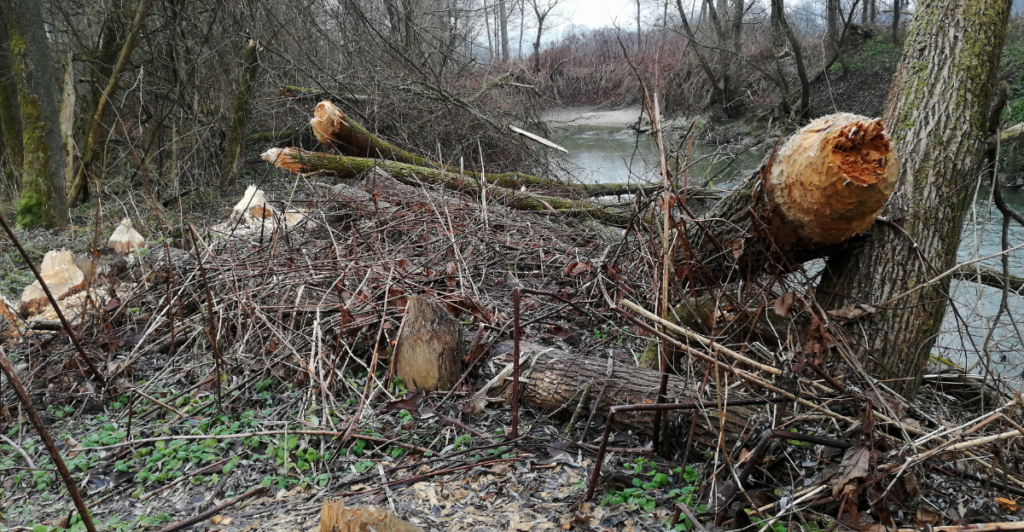

The wolf-beaver dynamic exemplifies the complexity of food webs and their cascading effects. Wolves preying on beavers can reshape wetlands, influencing water storage and habitat availability. Wetlands that dry up due to beaver absence affect amphibians, fish, and bird species reliant on these environments. Nutrient cycling and hydrology are also disrupted, impacting plant and animal communities. These effects highlight the profound influence predators have on ecosystems, shaping habitats and species distributions in ways that ripple across multiple ecological levels.
Conservation Considerations

Understanding the interaction between wolves and beavers is essential for conservation efforts. Wolves’ predation on beavers demonstrates the intricate balance between species and ecosystems. Conservation plans must account for these relationships to avoid unintended consequences. Over-managing one species can disrupt another, altering habitats and biodiversity. Protecting both wolves and beavers ensures ecosystem health and resilience. By studying their interactions, researchers can guide policies that promote coexistence, emphasizing the value of preserving predator-prey dynamics for maintaining ecological balance in natural landscapes.
Future Research Directions

Future studies should focus on the long-term ecological impacts of wolf predation on beaver populations. Key questions include how this predation affects wetland persistence, biodiversity, and the broader hydrological cycle. Researchers could also investigate how climate change influences these dynamics, potentially altering predator-prey interactions. Advancing technology, such as GPS tracking and ecological modeling, can deepen our understanding. These efforts will not only provide insights into wolf and beaver behavior but also inform conservation strategies for managing these critical species in changing environments.
Unique Relationship
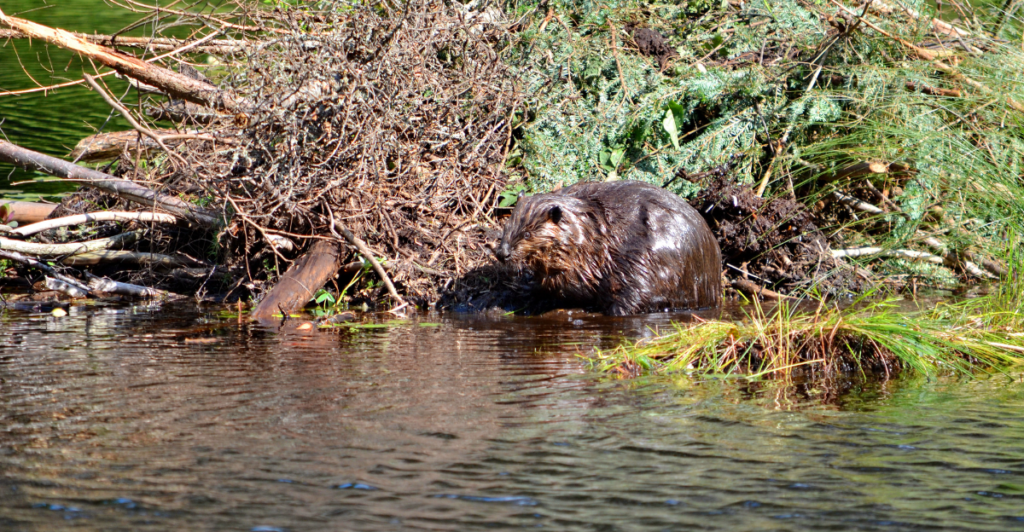

The unique relationship between wolves and beavers highlights the intricate connections within ecosystems. Wolves’ ambush tactics and beavers’ ecosystem-engineering roles create a fascinating interplay of survival and environmental influence. This predator-prey dynamic shapes landscapes, affects biodiversity, and underscores the importance of ecological balance. By studying these interactions, researchers gain valuable insights into the complexity of nature. Protecting both species ensures the continuation of these dynamic processes, demonstrating the essential role predators and prey play in maintaining the health of our planet’s ecosystems.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed
12 Bold Animals That Have No Fear of Predators – Nature’s Underrated Fighters
12 Little-Known Predators That Keep U.S. Ecosystems in Check
Bobcats Are Making a Comeback—And They Might Be Protecting Us From Disease
Top States Where Wolverines Still Roam
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







