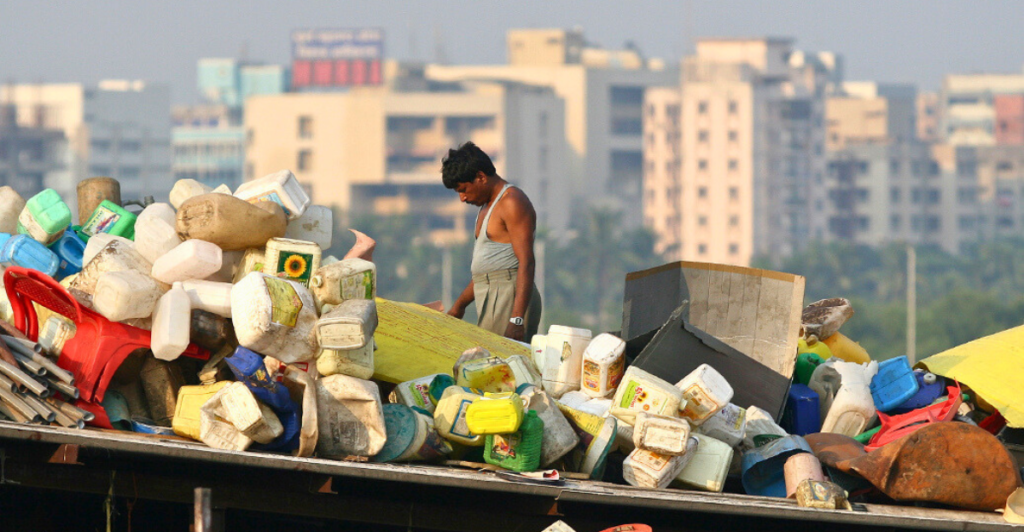

Scientists discovered a mutant enzyme capable of breaking down plastic at an unprecedented rate while researching ways to tackle the global plastic waste crisis. The enzyme, derived from bacteria found in a Japanese recycling plant, could revolutionize how we deal with non-biodegradable plastics. Accelerating decomposition can significantly reduce the environmental impact of plastic pollution. Here’s everything you need to know about this fascinating discovery.
What Is the Mutant Enzyme?
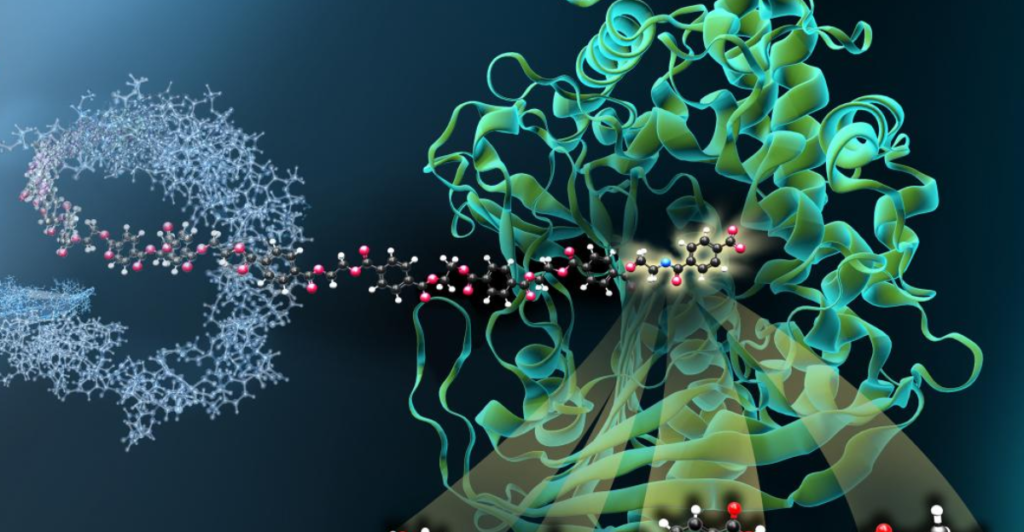
The enzyme PETase targets polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a standard plastic in bottles and packaging. PET typically takes hundreds of years to decompose in the environment. However, PETase speeds up the process significantly. Scientists altered the enzyme’s structure during a study, accidentally enhancing its plastic-degrading properties. This mutation could pave the way for innovative recycling solutions and reduce the reliance on traditional plastic disposal methods like incineration and landfilling.
The Accidental Discovery
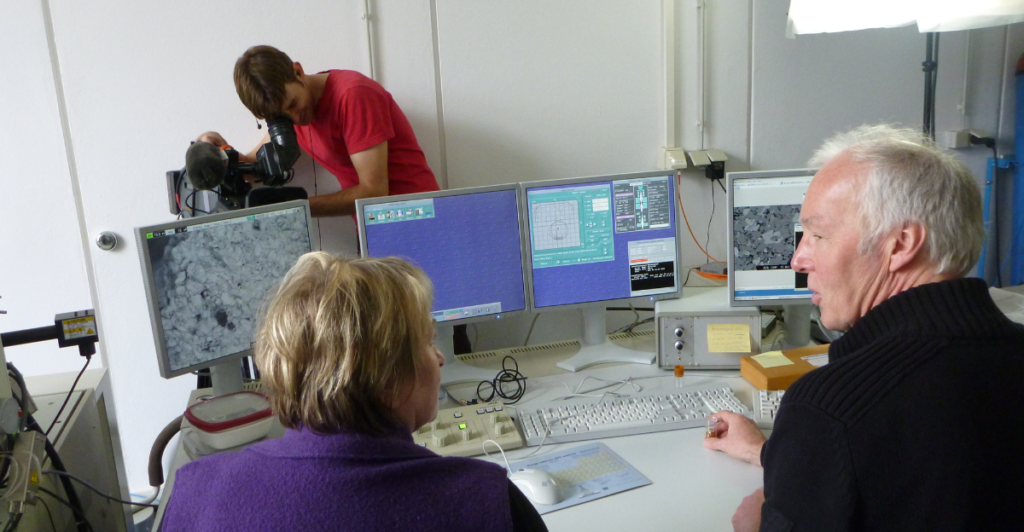

This groundbreaking enzyme was discovered in 2016 when researchers analyzed bacteria at a waste recycling site in Japan. While attempting to study the natural degradation process of PET, they unintentionally engineered a more efficient version of the enzyme. This accidental modification has spurred hope for addressing the growing mountains of plastic waste worldwide, proving that science often progresses unexpectedly.
How PETase Works
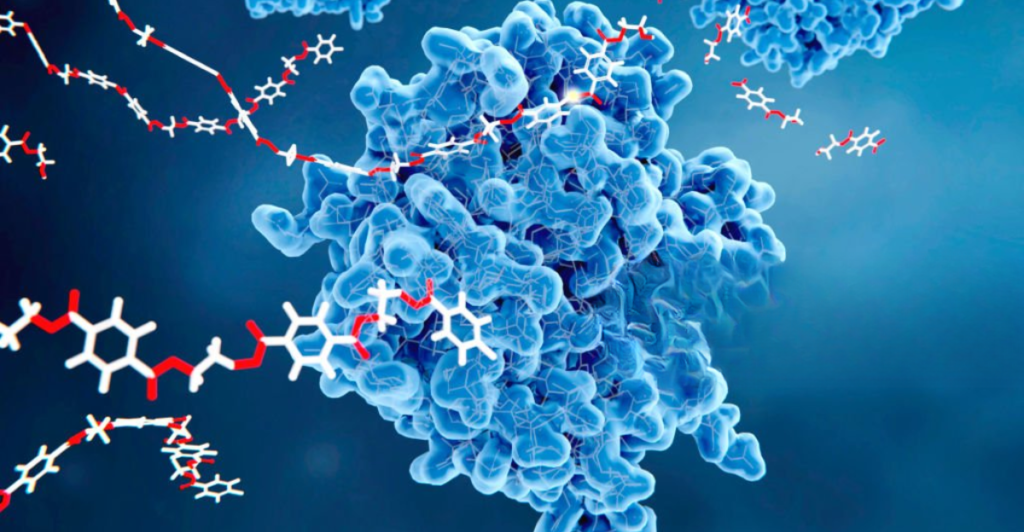
PETase breaks down plastic by targeting its molecular structure. PET is made of long chains of repeating chemical units. PETase interacts with these chains, breaking them into smaller, biodegradable molecules. This process, known as depolymerization, mimics how natural enzymes break down organic matter. PETase could process plastics more efficiently, unlike traditional recycling methods, even in environments with minimal resources, offering a glimpse into sustainable plastic management.
Benefits of PETase

One significant benefit of PETase is its potential to reduce plastic waste accumulation. Unlike traditional recycling, which often downgrades plastic quality, PETase breaks it into raw materials to create new products. This process, called closed-loop recycling, preserves the quality of materials. Additionally, PETase’s efficiency could make recycling more cost-effective, encouraging widespread adoption and less reliance on non-renewable resources for manufacturing new plastics.
Challenges Ahead
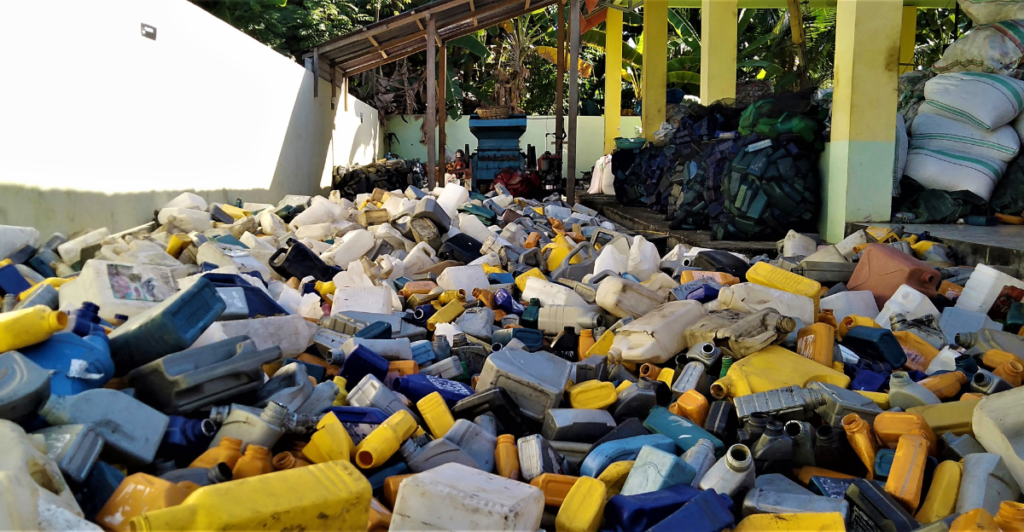

Despite its potential, PETase faces several challenges before large-scale implementation. Current enzyme efficiency, while impressive, still needs improvement for industrial use. Critical hurdles are scaling up production, optimizing conditions, and ensuring economic feasibility. Furthermore, addressing different types of plastics beyond PET remains a complex task. Scientists are enhancing the enzyme’s performance to meet these demands while maintaining environmental safety.
Environmental Impact

Plastic pollution has dire consequences for ecosystems, wildlife, and human health. PETase could mitigate these effects by reducing the amount of plastic in landfills and oceans. By breaking down existing plastic waste, the enzyme offers an alternative to traditional disposal methods that often release harmful chemicals or microplastics. Adopting biotechnological innovations could lead to a cleaner, healthier planet for future generations.
What Makes This Unique?

While other biological methods exist for breaking down plastic, PETase stands out due to its efficiency and specificity for PET. Previous methods were slower or required extreme conditions, making them impractical for widespread use. PETase’s accidental improvement opens doors to practical applications in recycling plants and beyond. Its discovery highlights the untapped potential of natural organisms and their derivatives in solving human-made environmental problems.
Potential Applications
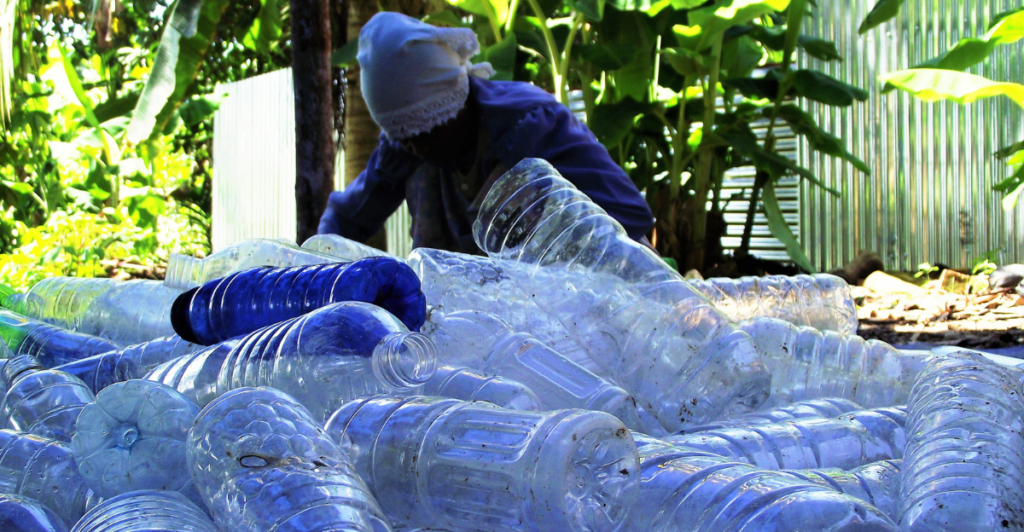

Beyond recycling plants, PETase can be used in various industries. Packaging manufacturers could incorporate enzyme-based recycling systems to process post-consumer waste directly. Coastal cleanup efforts might deploy PETase to target ocean plastics. Additionally, the enzyme’s success could inspire similar innovations for other hard-to-recycle materials, extending its impact beyond PET. These applications could redefine waste management practices globally.
Collaborations and Research

International teams of scientists are collaborating to refine PETase for real-world use. Researchers use advanced protein engineering and artificial intelligence techniques to enhance the enzyme’s plastic-degrading capabilities. By sharing findings and resources, these partnerships aim to accelerate the enzyme’s transition from laboratory success to environmental solution, underscoring the importance of global cooperation in addressing environmental challenges.
Broader Implications for Science

The accidental creation of PETase illustrates how unexpected discoveries can lead to groundbreaking solutions. It highlights the importance of fundamental research and experimentation and underscores the role of biotechnology in solving modern challenges. As scientists continue to explore the natural world, more discoveries like PETase could emerge, offering innovative ways to tackle pressing global issues, from pollution to energy shortages.
Public Reception

The public and environmental advocates have responded enthusiastically to PETase’s potential. Many see it as a beacon of hope in the fight against plastic pollution. However, some have expressed caution, emphasizing the need to address potential risks and ensure the technology is applied responsibly. Transparency and collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and the public will be essential for building trust and maximizing its benefits.
A Step Toward a Greener Future

The discovery of PETase represents a significant step toward sustainable waste management. While challenges remain, its potential to transform recycling and reduce plastic pollution is undeniable. By continuing to invest in research and innovation, society can leverage such breakthroughs to create a cleaner, more sustainable world. PETase’s story serves as a reminder that even small discoveries can lead to monumental changes.
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







