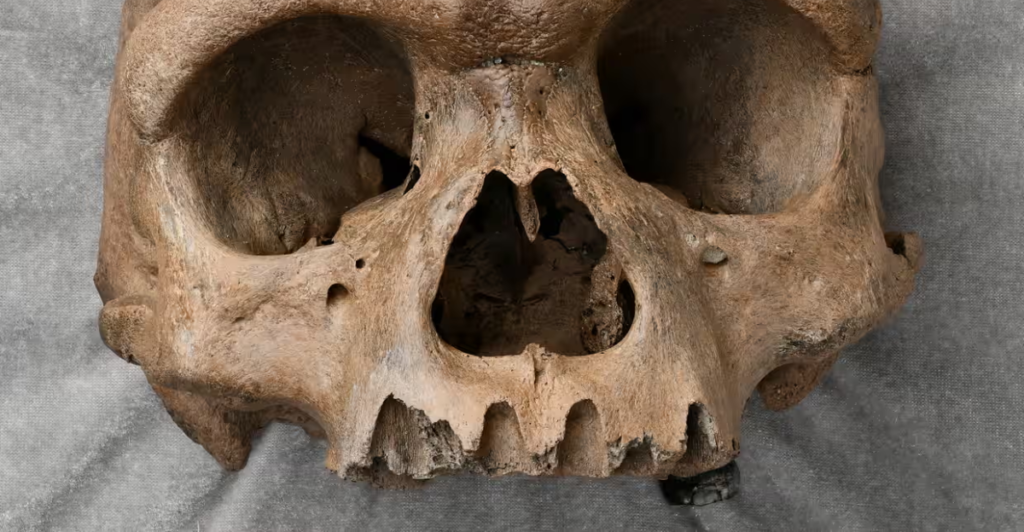
In 2023, researchers unearthed a mysterious skull in a cave near Hualongdong, China. The fossil, nicknamed “Dragon Head,” captivated scientists with its peculiar features, blending archaic and modern traits. With its massive cranial capacity and pronounced brow ridge, the skull hinted at a previously unknown hominid species. Found alongside primitive tools and animal remains, the site provided clues about the creature’s lifestyle. This discovery marked a turning point in understanding Asia’s role in human evolutionary history.
Unique Features of the Fossil
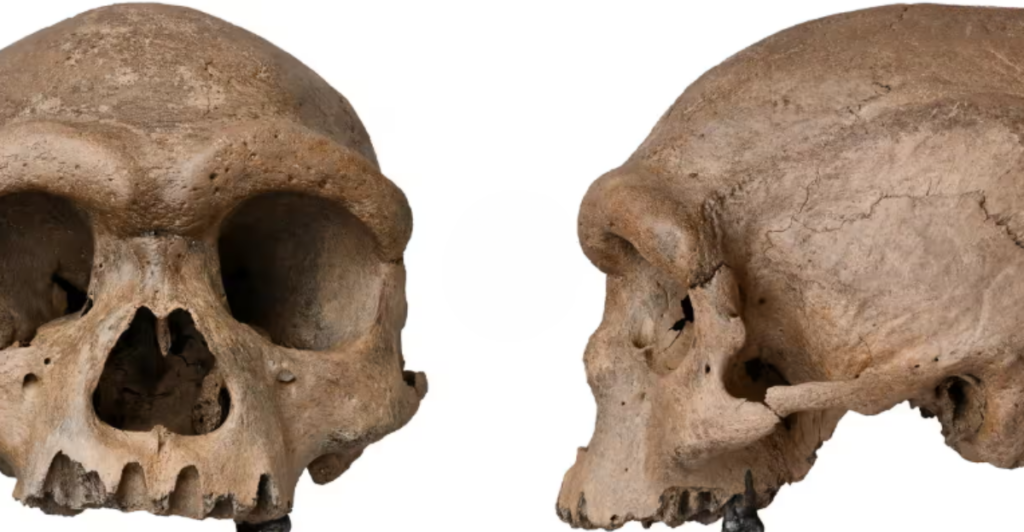

The Dragon Head skull exhibits a fascinating blend of characteristics, such as a large cranial size, robust jawline, and thick brow ridge, distinct from modern humans and Neanderthals. Its unique morphology has perplexed scientists, leading to debates about its classification. Researchers noted its potential to represent a hybrid species or a separate lineage altogether. This fossil challenges previous assumptions, suggesting evolutionary diversity in Asia during the period when early Homo sapiens emerged.
Context of the Discovery

The fossil was unearthed in a cave system in southeastern China, a region known for its rich archaeological sites. Surrounding artifacts, such as rudimentary stone tools and charred bones, indicate that the hominid used fire and basic hunting techniques. Radiometric dating places the skull at approximately 300,000 years old. This timing coincides with the emergence of Homo sapiens in Africa, raising questions about parallel evolutionary developments on different continents.
Challenging the Out of Africa Theory

For decades, the “Out of Africa” theory posited that modern humans originated in Africa and spread across the globe. However, the Dragon Head fossil suggests Asia may have hosted its own evolutionary experiments. Some researchers argue this hominid could have interbred with Homo sapiens or even contributed to modern human DNA. The discovery highlights a potentially more intricate web of migrations and interactions than previously believed.
Connections to Other Asian Hominids

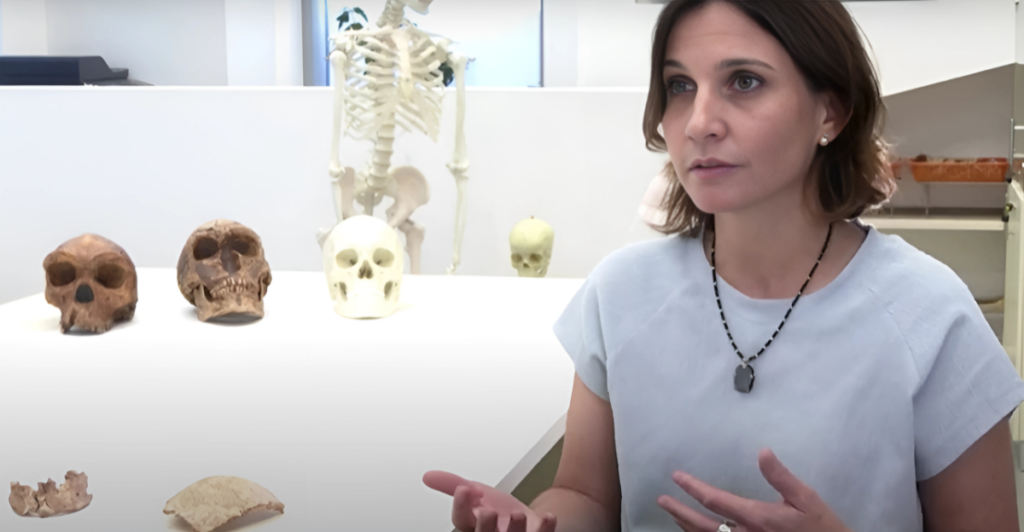
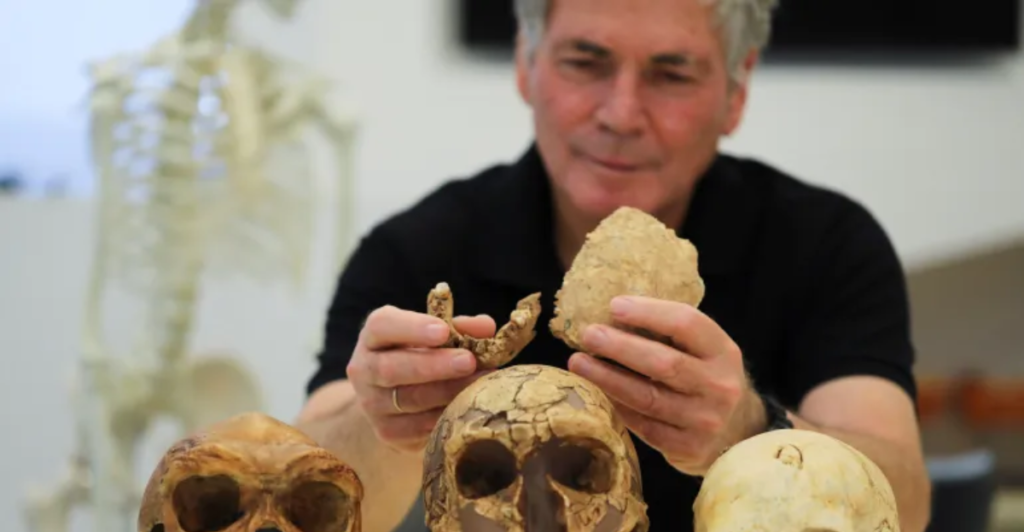
The Dragon Head fossil is part of a growing body of evidence pointing to hominid diversity in Asia. Comparisons with fossils like the Dali Man and Denisovans reveal shared traits, such as robust cranial features and advanced tool use. These similarities suggest that Asia was not just a migration corridor but a significant site for evolutionary innovation, complicating the traditional view that Africa was the sole cradle of humanity.
Genetic Revelations

DNA analysis of the Dragon Head fossil is underway, with hopes of uncovering links to modern humans or other archaic hominids. Genetic material could reveal whether this species interbred with Homo sapiens or Denisovans, adding to the mosaic of human ancestry. Preliminary findings hint at unique genetic markers, potentially rewriting the story of how different human species interacted and evolved.
Impact on Anthropology

The discovery has sparked intense debates within the anthropological community. While some experts embrace the implications of a complex evolutionary narrative, others urge caution until more evidence is uncovered. The fossil’s unique features and location are prompting a re-examination of archaeological sites across Asia, emphasizing the need for a global perspective in human evolutionary studies.
Local and Global Reactions
The Dragon Head fossil has been celebrated in China as a symbol of the nation’s rich prehistoric heritage. Internationally, the discovery has drawn both excitement and skepticism, with scientists calling for additional research to confirm its significance. The find underscores the importance of cross-border collaboration in uncovering humanity’s shared past.
Technology’s Role in the Discovery

Cutting-edge technology played a crucial role in analyzing the Dragon Head fossil. 3D imaging allowed researchers to reconstruct the skull and identify its unique traits, while advanced dating methods established its age. Artificial intelligence is being employed to compare the fossil with global databases, offering unprecedented insights into its evolutionary significance.
Implications for Human Migration

The Dragon Head discovery suggests a more dynamic model of human migration. Asia may have been more than a transit route—it could have been a hub for evolutionary development. The fossil supports the idea that multiple hominid species coexisted, migrated, and interbred, creating a more intricate picture of humanity’s origins.
Cultural Significance
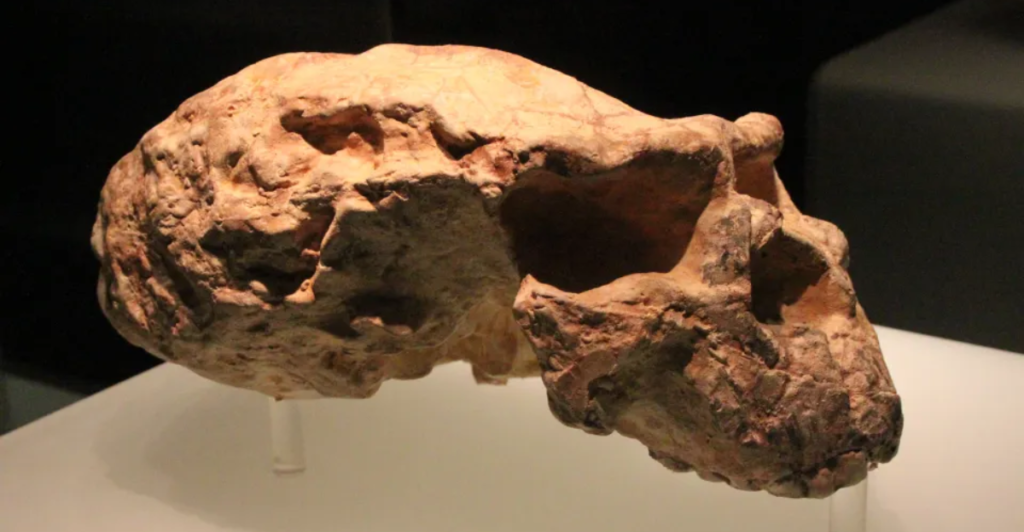

The Dragon Head fossil has sparked curiosity and pride in China, highlighting the region’s contribution to understanding human evolution. Local communities are engaging with the discovery through museum exhibits and educational programs, fostering a deeper appreciation for their prehistoric heritage and its global importance.
Future Research Directions
The Dragon Head discovery has paved the way for new excavations across Asia. Researchers are targeting similar cave systems in hopes of uncovering additional fossils that could shed light on this enigmatic species. Collaborative efforts are expanding, combining expertise from anthropology, genetics, and technology to unlock more secrets of ancient humanity.
A New Chapter in Human History
The Dragon Head fossil is a reminder that the story of human evolution is far from complete. Its discovery challenges long-held beliefs and highlights the complexity of our ancestry. As research continues, the Dragon Head may prove to be a critical piece of the puzzle, reshaping our understanding of where we come from and the interconnected paths that led to modern humanity.
Sources:
Fossils found in Chinese cave could shed new light on origins of modern humans
Scientists discover lost ‘big head’ human species in Asia: study
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







