
Crows continue to challenge what scientists thought they knew about animal intelligence. These remarkable birds have consistently showcased abilities that rival and sometimes surpass, those of other species, including humans. A groundbreaking study revealed that crows can understand recursion, the ability to embed structures within similar structures. Previously thought to be a unique hallmark of human language, recursion allows for forming complex sentences. Crows mastered this skill during experiments, performing as well as young children.
What Is Recursion?

Recursion is a mental process critical to understanding human language. For instance, in the sentence, “The mouse the cat chased ran,” one clause is nested within another. For decades, recursion was considered a uniquely human cognitive skill, until now.
Recursion Beyond Humans

While monkeys have shown some ability for recursion with training, crows achieved similar results with less guidance. This challenges the belief that advanced cognition is exclusive to mammals or primates.
Crows as Toolmakers
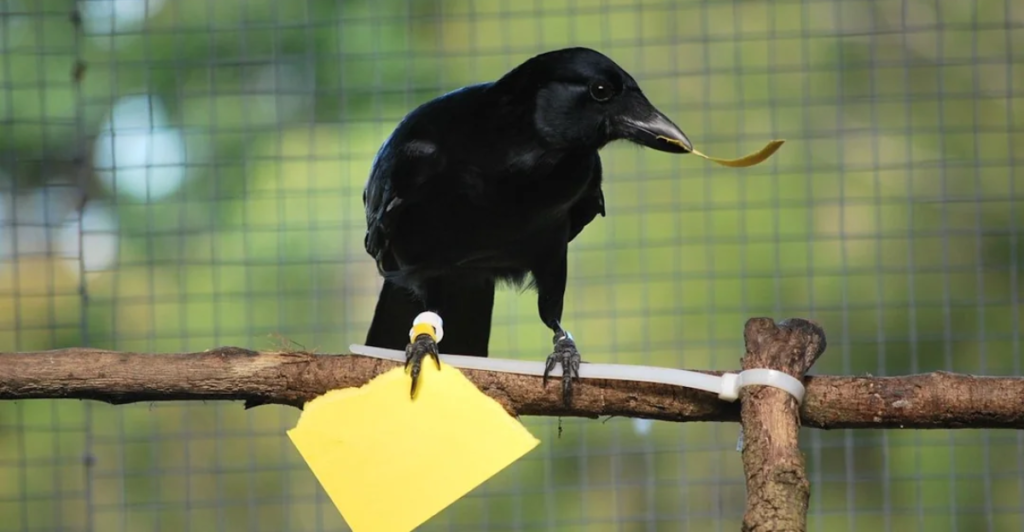

Crows are famously adept at making and using tools. New Caledonian crows, for example, craft tools like hooked twigs and spiked leaves to extract food. Their tool-making process involves planning and innovation, traits once considered human-exclusive.
A Cognitive Mood Boost

Using tools doesn’t just solve problems for crows. It makes them optimistic. Researchers found that crows who successfully used tools displayed faster, more enthusiastic responses to ambiguous challenges, indicating a positive emotional state.
Pattern Recognition or True Understanding?

Critics argue that crows might rely on associative learning rather than grasping concepts like recursion. However, when the complexity of tasks increased, the birds’ success suggested genuine cognitive understanding rather than mere memorization.
Evolutionary Implications

Crows and primates diverged evolutionarily millions of years ago. Yet, both exhibit advanced cognitive skills. This suggests either an ancient shared trait or convergent evolution, where unrelated species develop similar abilities to tackle common challenges.
The Brain Without a Neocortex

Unlike mammals, crows lack a neocortex, the brain region associated with higher cognition. Instead, their densely packed neurons in other brain areas allow them to perform complex tasks, highlighting alternative pathways to intelligence.
Social Navigation and Problem Solving

Recursion could serve purposes beyond communication for crows. It might help them navigate intricate social hierarchies or predict others’ behavior, showcasing the versatility of this cognitive skill.
Breaking the Bird Brain Myth
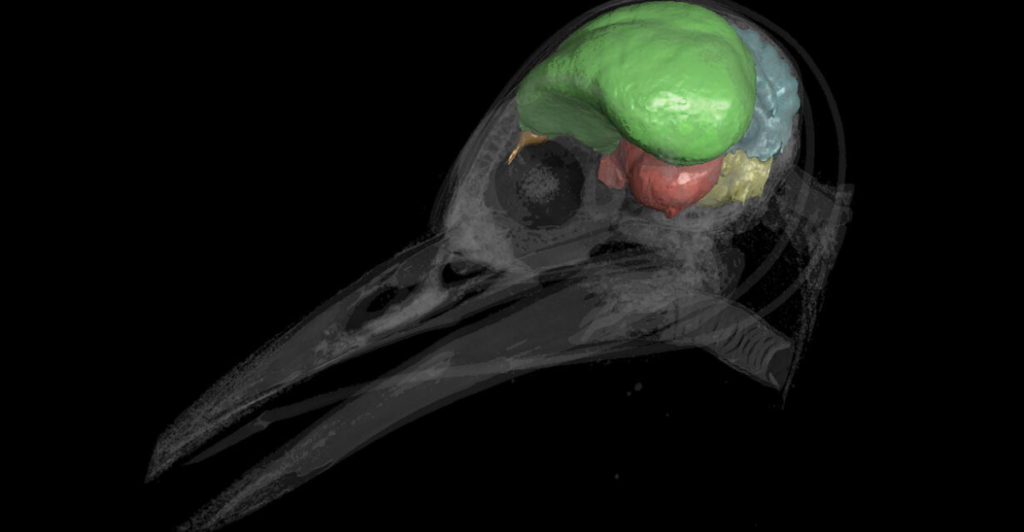
For years, birds were underestimated due to their small brain size. Now, studies reveal that bird brains are incredibly efficient, packing dense clusters of neurons that rival primate brains in functionality.
Play for Pleasure
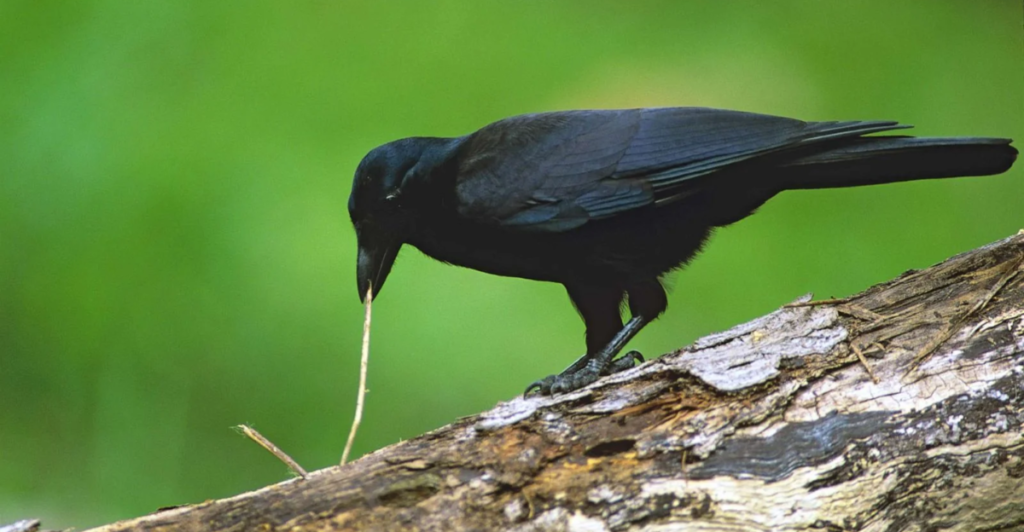

Crows use tools not just for survival but also for fun. Researchers observed that tool use seems to bring intrinsic joy, akin to how humans enjoy games or art. This adds a new layer to understanding animal emotions.
Emotional Intelligence in Animals
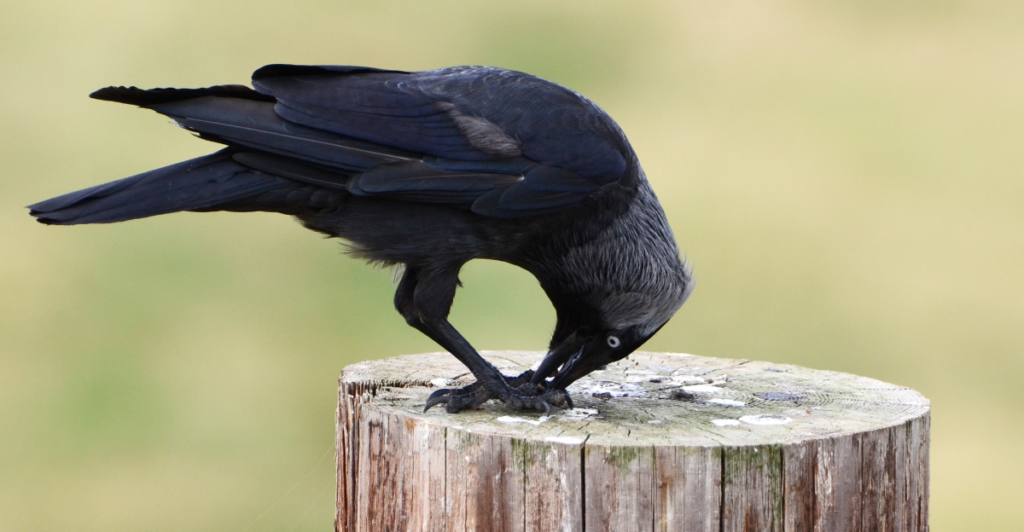

The study of crows’ emotional responses to tools challenges outdated notions of animals as mere instinct-driven beings. It underscores that emotions, cognition, and behavior are deeply interconnected across species.
The Bigger Picture: What Else Can They Do?

Crows continue to surprise scientists with feats like recognizing human faces, solving puzzles, and even engaging in behaviors resembling cultural practices. They have proven time and again that intelligence is not confined to humans or mammals. By exploring their capabilities, scientists not only learn about these incredible birds but also uncover deeper insights into the nature of cognition itself. What will crows teach people next? The sky, quite literally, is the limit.
References:
Crows, with their sleek black feathers and sharp intelligence, have long been a subject of fascination for humans.
Crows Know How to Have Fun
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







