
California’s Joshua trees are in peril due to wildfires, urban expansion, and climate change. To combat these threats, the state has implemented a bold conservation plan. Let’s explore the steps California is taking to secure the future of these iconic desert plants.
Why Are Joshua Trees at Risk?

The Western Joshua tree is battling multiple challenges, including wildfires, habitat loss, and an ever-warming climate. Rising temperatures and irregular rainfall patterns make the Mojave Desert less hospitable, while invasive species and human activities, such as off-roading and pesticide use, further degrade their environment. Without intervention, experts warn the majority of Joshua tree habitats could vanish by 2100, leaving behind a weakened ecosystem dependent on their survival.
The Conservation Act That Changed Everything

California’s Western Joshua Tree Conservation Act passed in 2023, marked a historic step in addressing climate-driven species loss. This law bans the removal, damage, or destruction of Joshua trees without state permits, creating legal safeguards for their survival. It also allocates resources to habitat conservation, restoration, and community collaboration, making Joshua trees the first species in California protected under climate-focused legislation.
A Comprehensive Plan for Survival
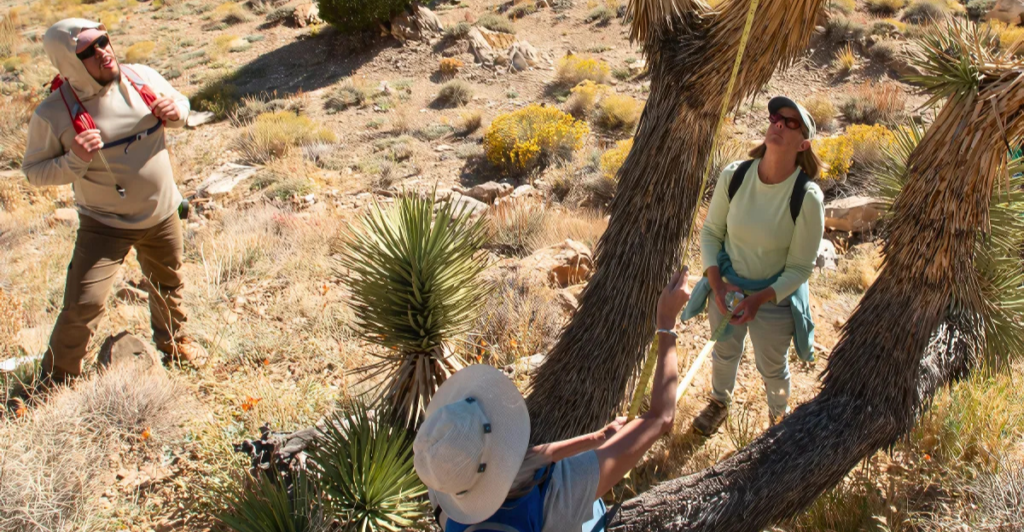

The California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) recently released a 294-page draft plan detailing actions to protect Joshua trees. Strategies include minimizing human disturbances, mitigating wildfire risks, and mapping future habitats that could withstand hotter, drier conditions. The plan also emphasizes the importance of conserving pollinators, like moths and small mammals, critical to Joshua trees’ reproduction.
Mapping Priority Lands
To secure the trees’ future, California aims to identify “priority conservation areas” by December 2025. These zones will focus on regions with the best conditions for Joshua trees to thrive in a warming climate. By 2033, the plan seeks to protect 70% of these areas through state purchases, conservation easements, and collaborations with private landowners.
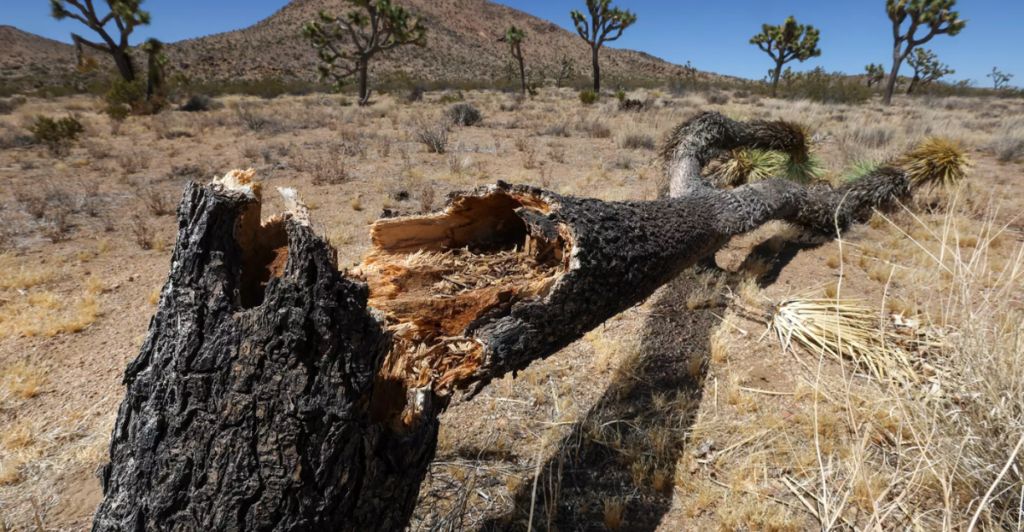
Fighting Wildfires and Rehabilitating Burned Areas
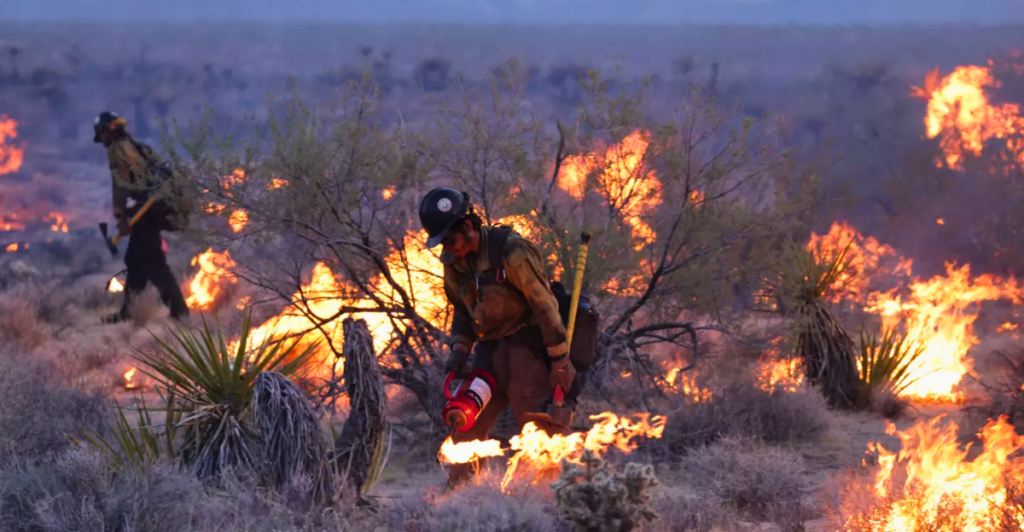

Wildfires are one of the greatest threats to Joshua trees, often wiping out entire populations. California’s plan includes fire prevention protocols, training for first responders to protect habitats, and post-fire restoration. Efforts also focus on removing invasive species like cheatgrass, which fuel wildfires, and replanting burned Joshua trees alongside other native vegetation.
Moving Joshua Trees to Safer Locations
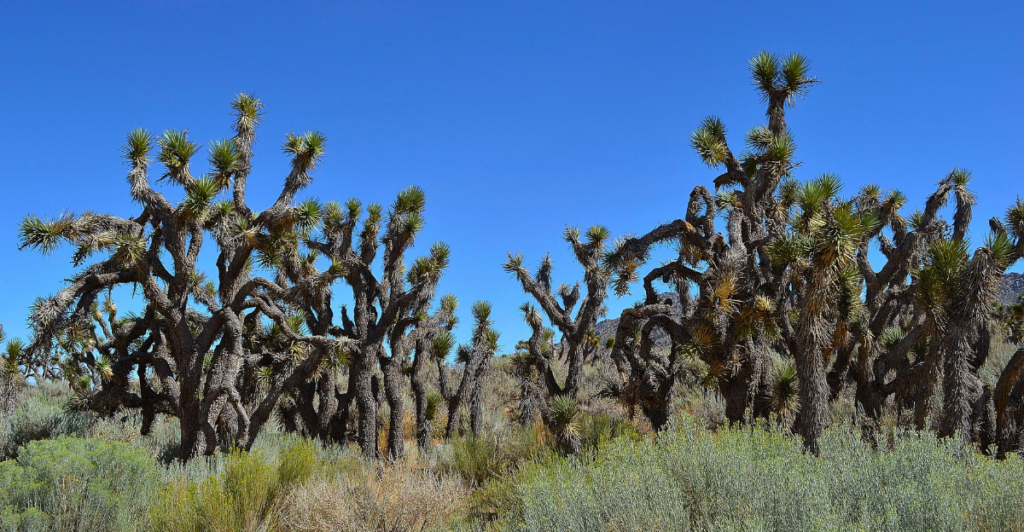

Relocating Joshua trees from high-risk areas to “climate refuges” is another strategy. These refuges are locations with stable, suitable conditions where the trees can survive and reproduce. Relocation involves carefully moving trees to areas with appropriate soil, moisture, and temperature conditions to maximize their survival potential in an unstable climate.
Using Science to Aid Adaptation
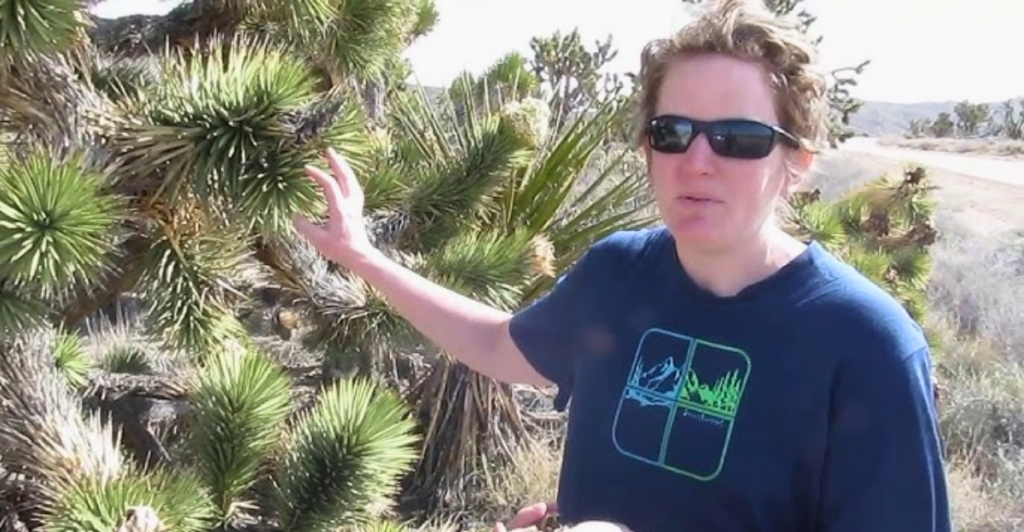

California is exploring assisted gene flow, a scientific method where genetically diverse Joshua tree populations better adapted to higher temperatures are introduced into conservation zones. This technique enhances genetic resilience, helping the trees withstand climate extremes and ensuring their ability to reproduce in changing environments.
Tribal Collaboration and Traditional Knowledge
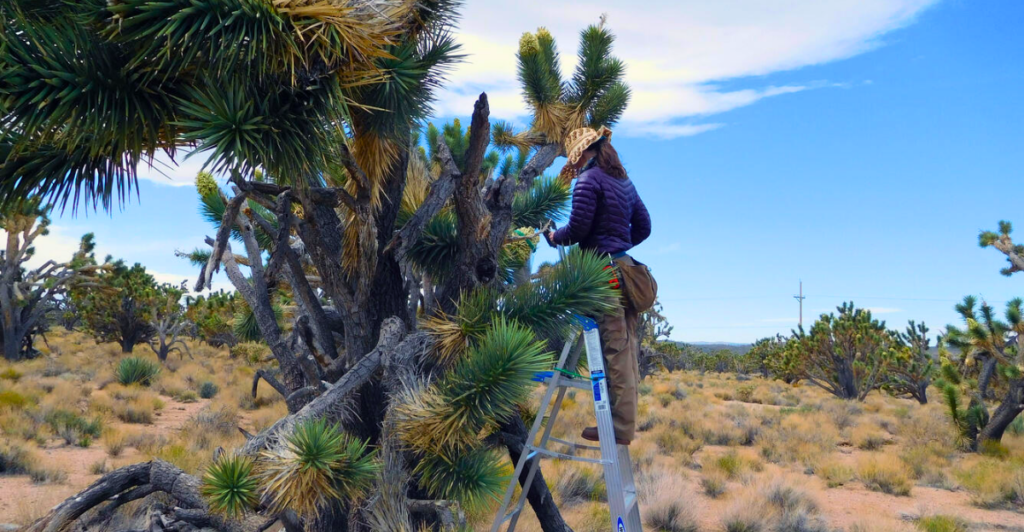

Indigenous communities play a key role in this conservation effort. California’s plan integrates traditional ecological knowledge, emphasizing time-tested stewardship practices. Tribal groups will work alongside scientists to manage habitats, restore degraded lands, and ensure cultural values are preserved while safeguarding the Joshua trees for future generations.
Educating and Engaging the Public
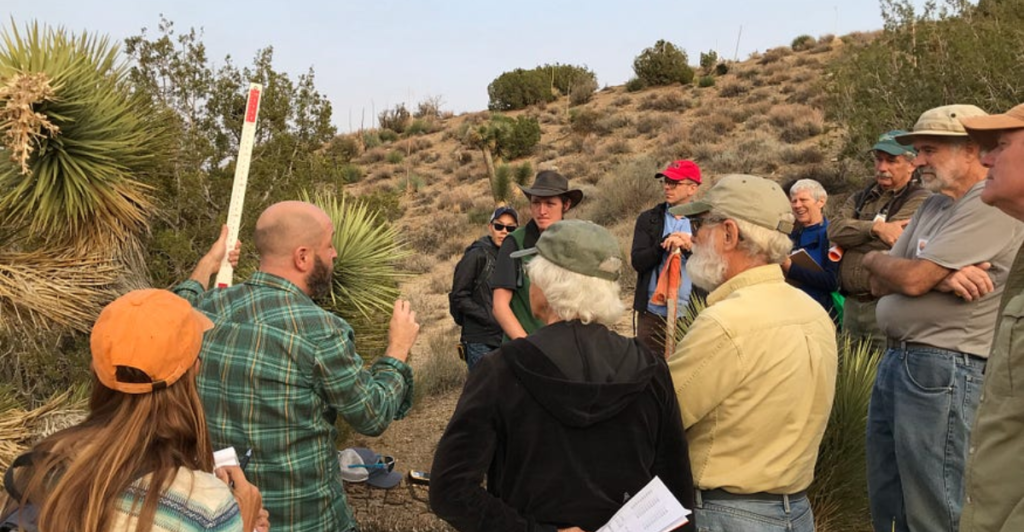

Public awareness campaigns aim to make Joshua tree conservation a shared mission. Outreach efforts include educational workshops, social media campaigns, and partnerships with schools to inspire the public to protect these symbolic trees. Increased awareness ensures more support for habitat conservation and policy implementation.
Securing Funding for Conservation

California has allocated $1.4 million to implement its Joshua tree conservation plan. This funding, combined with developer permit fees, supports monitoring, land acquisition, and habitat restoration. These financial resources are critical to achieving the plan’s long-term goals, including the protection of priority zones and post-fire recovery efforts.
The Role of Climate Change in This Fight

While the plan addresses many challenges, climate change remains the biggest obstacle. Without global action to curb greenhouse gas emissions, much of the tree’s habitat could disappear by 2100. The plan acknowledges that even the best local strategies depend on worldwide efforts to reduce emissions and mitigate climate impacts.
Balancing Conservation and Development

Some stakeholders worry about how the plan might affect economic activities, particularly in desert communities. Striking a balance between conservation and development is critical. Permits for tree removal, paired with conservation fees, are designed to offset potential economic losses while preserving essential habitats.
A Race Against Time

California aims to finalize its Joshua tree conservation plan by mid-2025. This timeline underscores the urgency of preserving a species threatened by climate change and human encroachment. By implementing science-driven solutions, the state hopes to protect both Joshua trees and the Mojave Desert ecosystem they anchor. This comprehensive approach showcases California’s commitment to saving Joshua trees and addressing climate-driven biodiversity loss. With these steps, the state aims to preserve an iconic symbol of resilience for generations to come.
References:
Joshua Trees Are in Peril. California Has a Plan to Save Them
California Has a New Plan to Save Imperiled Joshua Trees
California’s Bold Strategy to Save Joshua Trees from Climate Crisis
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







