
In the intricate web of life on Earth, certain species play pivotal roles that sustain ecosystems and, by extension, human existence. These organisms contribute to essential services such as pollination, oxygen production, and disease regulation. However, human activities have precipitated unprecedented rates of biodiversity loss, threatening these critical species and the benefits they provide.
A 2019 United Nations report revealed that around 1 million animal and plant species are now threatened with extinction, many within decades, more than ever before in human history. This alarming trend underscores the urgency of recognizing and preserving the species upon which humanity depends.
Bats
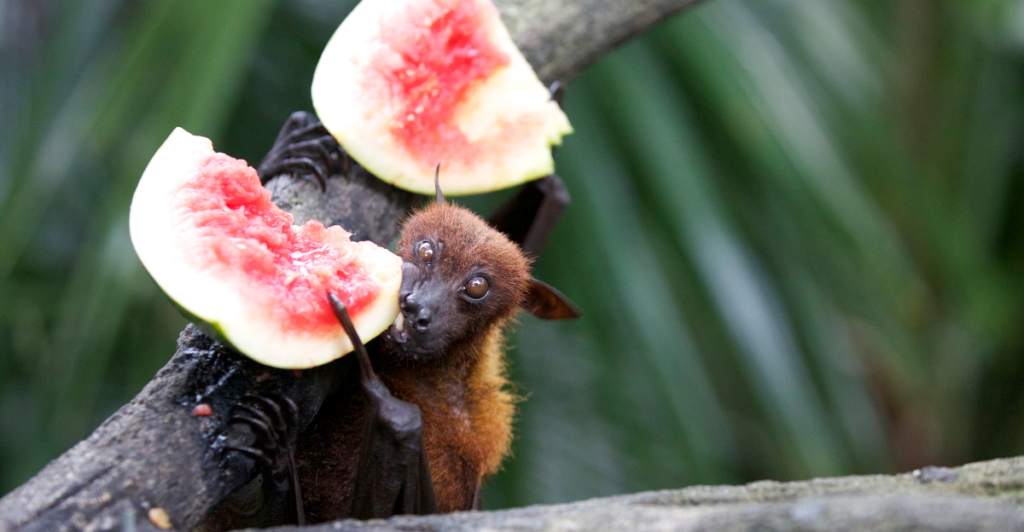

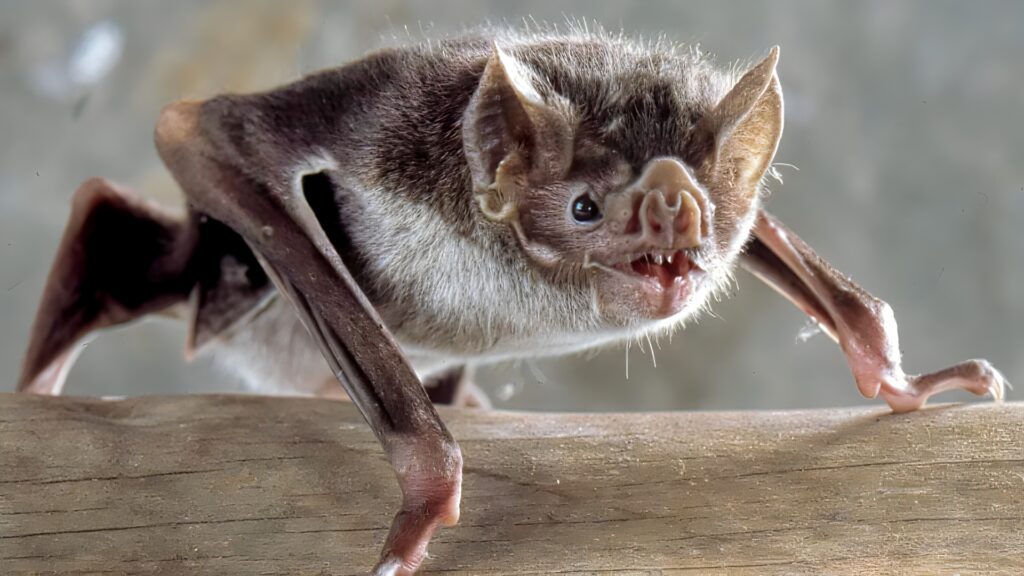
Beyond their role in pollination and seed dispersal, bats are natural pest controllers, consuming vast quantities of insects nightly. This predation helps regulate insect populations, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and supporting agricultural health. Unfortunately, bat populations are declining due to habitat destruction, diseases like white-nose syndrome, and human disturbances, which could lead to increased crop pests and associated challenges.
Honeybees (Apis mellifera)
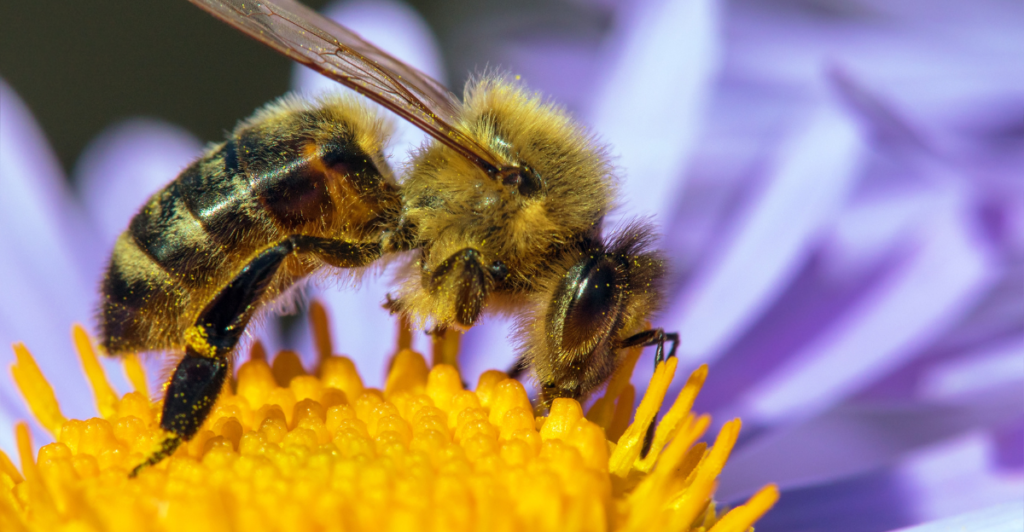

Honeybees are paramount among pollinators, facilitating the reproduction of approximately 75% of the world’s flowering plants and 35% of global crop production. Their pollination services are indispensable for fruits, vegetables, and nuts, directly influencing food security and nutrition. Alarmingly, honeybee populations have been declining due to factors like habitat loss, pesticides, and climate change, posing a significant threat to global agriculture.
Phytoplankton
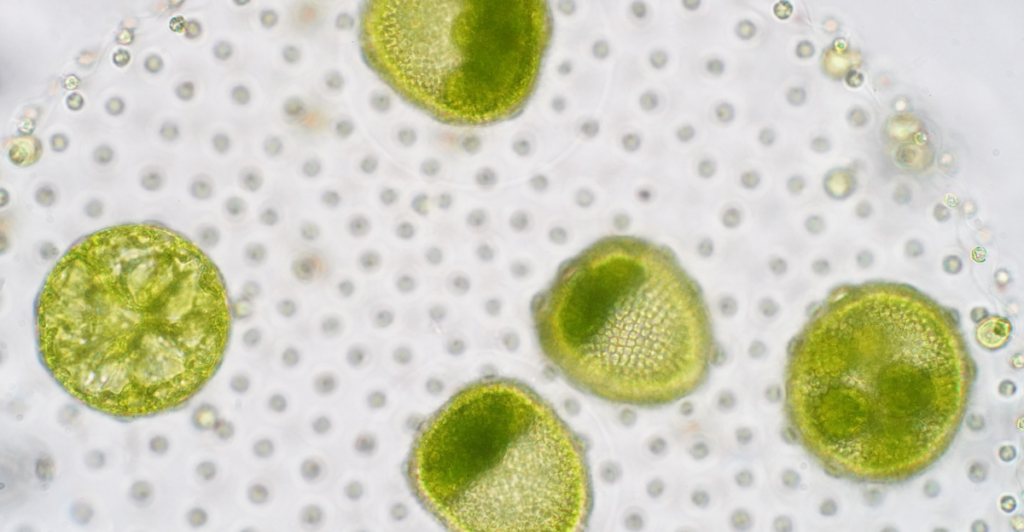
These microscopic marine organisms are the unsung heroes of oxygen production, generating about 50% of the Earth’s oxygen through photosynthesis. Phytoplankton also form the foundation of aquatic food webs, supporting a vast array of marine life. However, ocean warming and acidification are disrupting phytoplankton populations, with potential repercussions for atmospheric oxygen levels and marine ecosystems.
Earthworms
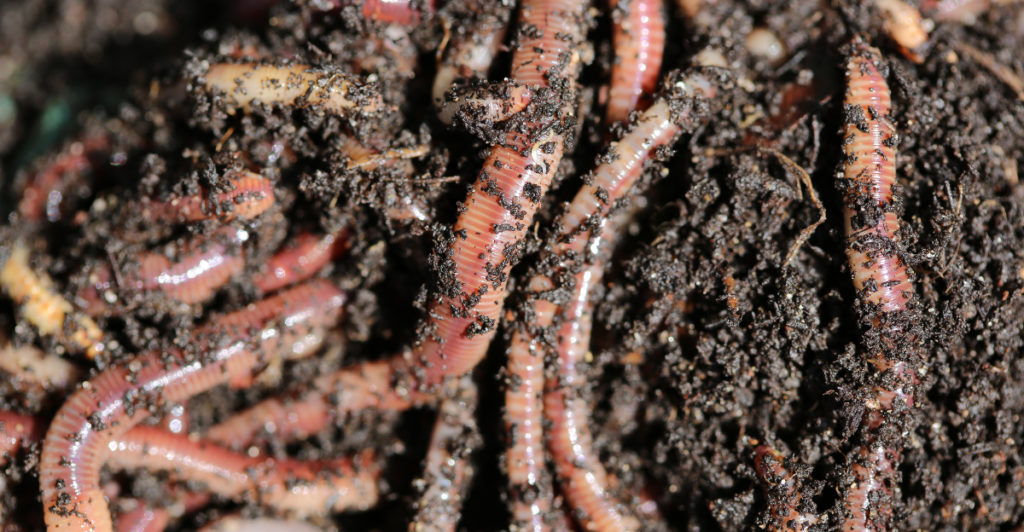

Often overlooked, earthworms are vital for soil health. Their burrowing aerates the soil, enhancing water infiltration and root growth, while their digestion of organic matter enriches soil fertility. Healthy soils are the cornerstone of productive agriculture, and the decline of earthworm populations due to soil pollution and intensive farming practices threatens this foundation.
Coral Reefs
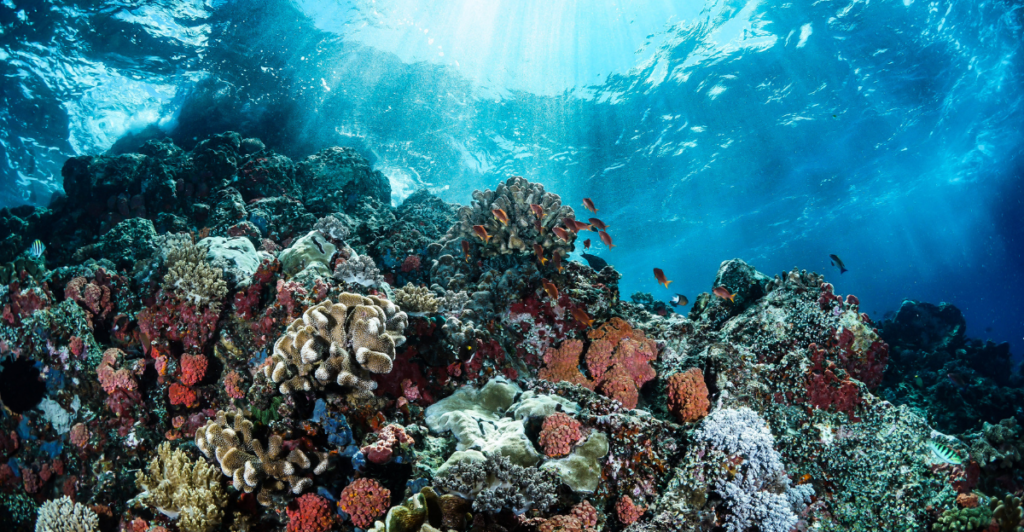

Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” support approximately 25% of all marine species. They provide coastal protection, support fisheries, and attract tourism, contributing significantly to local economies. However, climate change-induced coral bleaching, pollution, and overfishing are leading to widespread coral decline, endangering the myriad benefits they offer.
Vultures
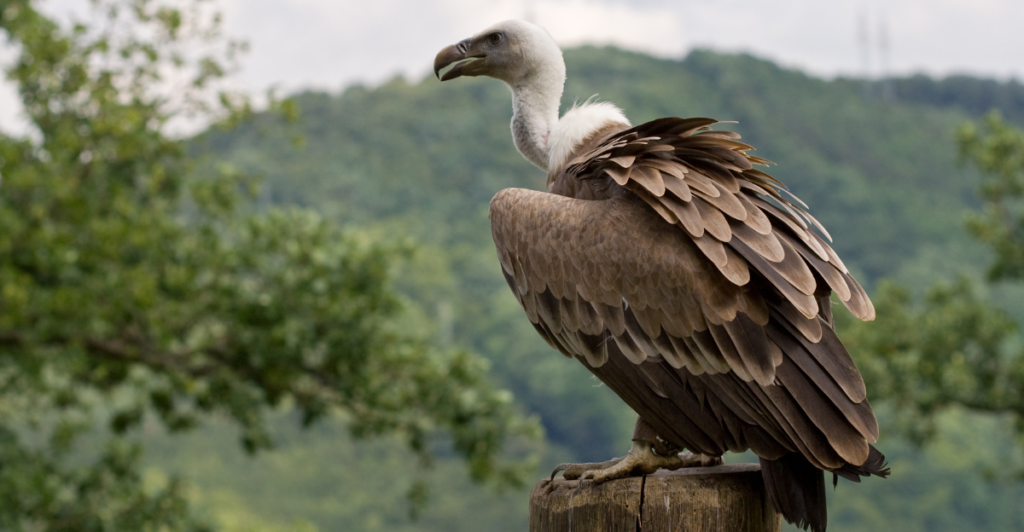

Vultures play a critical role in ecosystems by consuming carrion, which helps prevent the spread of diseases. Their efficient scavenging cleanses the environment of potential pathogens, protecting both wildlife and human populations. Declines in vulture populations, particularly in Asia and Africa, have been linked to increased carcass decomposition times and subsequent disease outbreaks, highlighting their importance in disease regulation.
Sea Otters
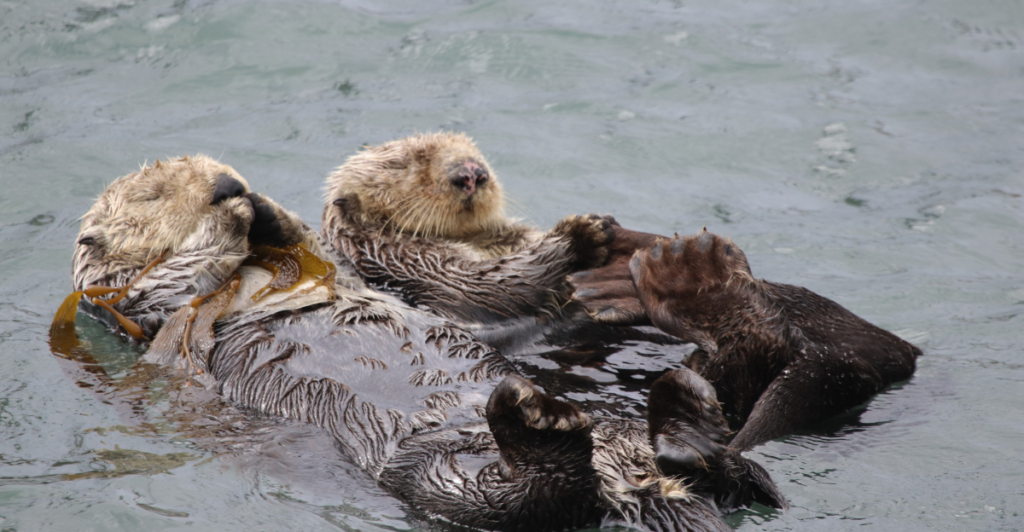

Sea otters are keystone predators in kelp forest ecosystems. By preying on sea urchins, they prevent overgrazing of kelp forests, which are vital carbon sinks and provide habitat for numerous marine species. The decline of sea otter populations can lead to the collapse of these ecosystems, reducing biodiversity and the ecological services they provide.
African Elephants
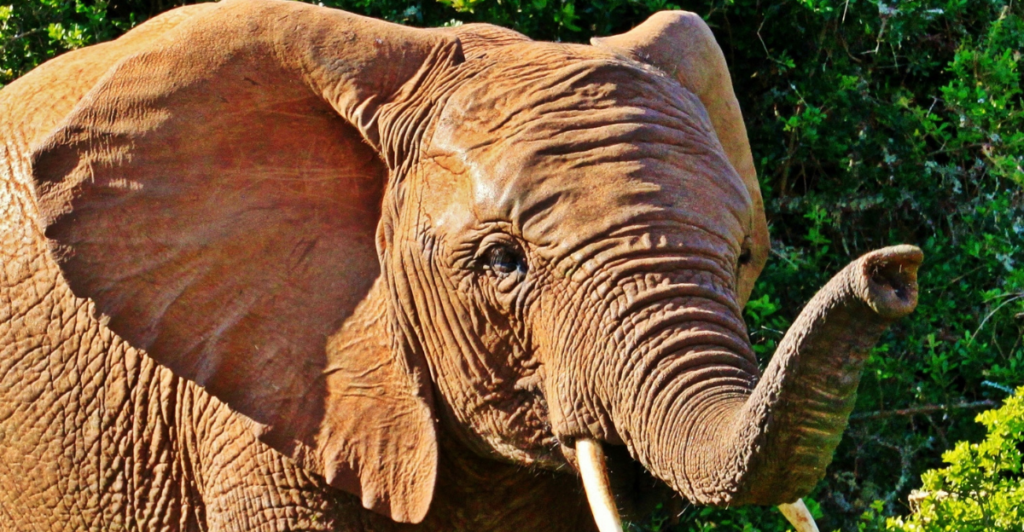

As mega-herbivores, African elephants shape their environments in ways that benefit numerous other species. Their foraging creates clearings that facilitate plant diversity, and their seed dispersal supports forest regeneration. Poaching and habitat loss have led to significant declines in elephant populations, with cascading effects on ecosystem health and resilience.
Fungi
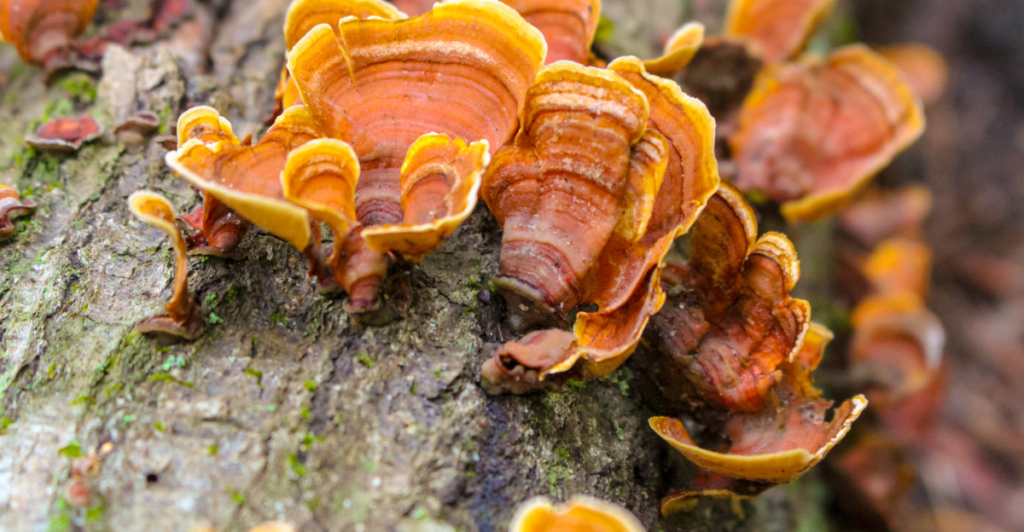

Fungi, including mycorrhizal fungi, form symbiotic relationships with plants, aiding in nutrient uptake and enhancing plant health. They are also crucial decomposers, breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients within ecosystems. The loss of fungal diversity due to pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change can impair these essential ecological processes, affecting plant communities and soil health.
The interdependence between humans and these species is a testament to the intricate connections that sustain life on Earth. The decline or loss of any of these organisms can disrupt ecosystems, diminish biodiversity, and compromise the services that underpin human survival.
Making A Difference

Addressing the threats to these species requires concerted global efforts, including habitat conservation, pollution reduction, sustainable agricultural practices, and climate change mitigation. Recognizing the invaluable roles these species play is the first step toward safeguarding the natural systems that support human life.
It’s Up To Us

The preservation of biodiversity is not merely an environmental concern but a fundamental necessity for human survival. By protecting these irreplaceable species, we ensure the continuity of the ecosystems that provide us with food, oxygen, disease regulation, and countless other benefits. The future of humanity is inextricably linked to the fate of these species; their survival ensures our own.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed.

Meet the Massive Crocodiles That Make Their Homes 40 Feet Underground
Fungus That Killed Millions Of Bats Now Found In Southern California—Farmers Worried
Top 10 Most Amazing Facts About Bats – Nocturnal Wonders
Bees Reportedly Halt Meta’s Plans for Nuclear-Powered AI Data Center
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







