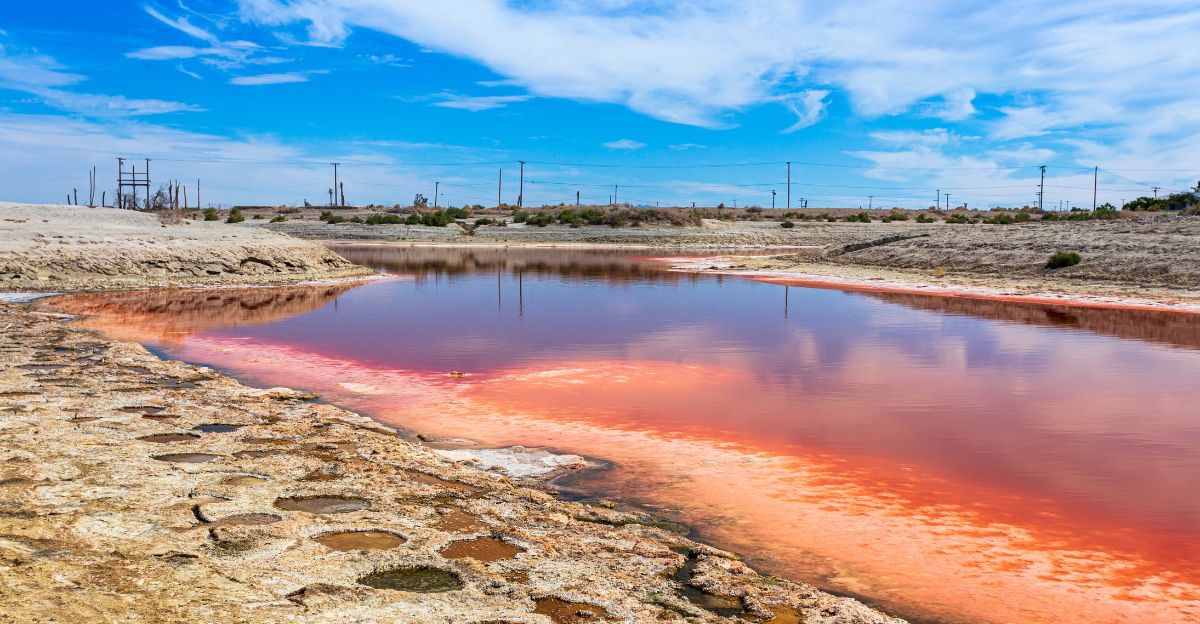

The Salton Sea, California’s largest lake, has long been a subject of fascination and concern due to its environmental challenges. However, a groundbreaking discovery has transformed this desolate body of water into a beacon of hope for America’s clean energy ambitions. Scientists have uncovered an astonishing 18 million tons of lithium—dubbed “white gold”—beneath its surface. This find has the potential to revolutionize the U.S. battery industry and significantly reduce reliance on foreign lithium imports.
A Pivotal Moment for Clean Energy
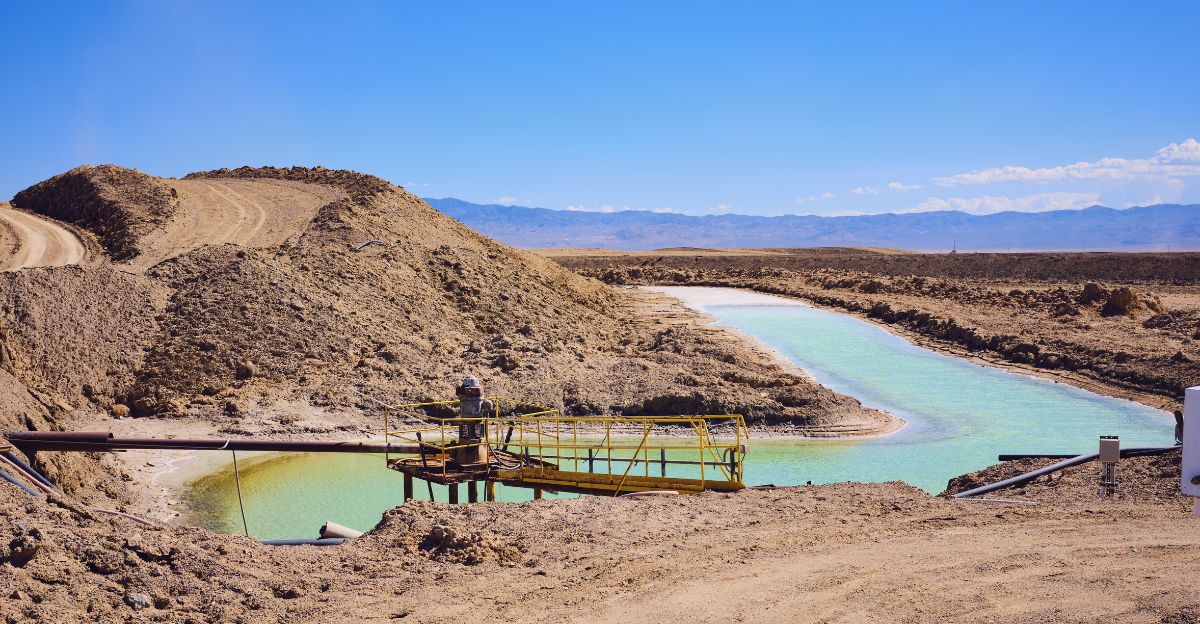

This discovery comes at a critical juncture as the world races to transition to electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy sources. The need for lithium, a crucial component in batteries, has surged, making this finding particularly timely. However, extracting this treasure trove presents numerous challenges, ranging from environmental risks to geopolitical implications.
A Lithium Bonanza Beneath the Surface

The Salton Sea, located in Southern California’s Imperial County, is now recognized as home to one of the largest lithium brine deposits globally. A recent study funded by the U.S. Department of Energy revealed that the lake contains an estimated 18 million tons of lithium, far exceeding the previously confirmed figure of 4 million tons. This amount could produce batteries for approximately 382 million electric vehicles—more than the total number of vehicles currently on U.S. roads.
Expert Insights on the Discovery
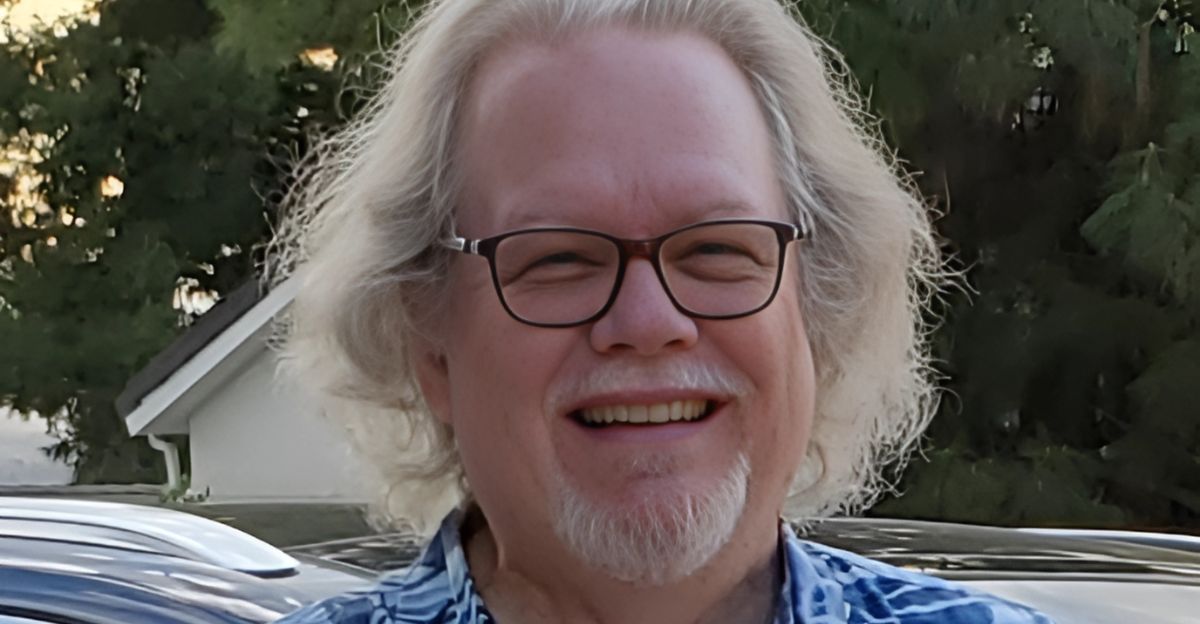

Michael McKibben, a geochemistry professor at the University of California, Riverside and one of the study’s authors, emphasized the significance of this discovery: “This is one of the largest lithium brine deposits in the world. This could make the United States completely self-sufficient in lithium and stop importing it through China.” California Governor Gavin Newsom has referred to the Salton Sea as the “Saudi Arabia of lithium,” underscoring its potential to position the U.S. as a global leader in lithium production.
The Challenges of Extracting “White Gold”
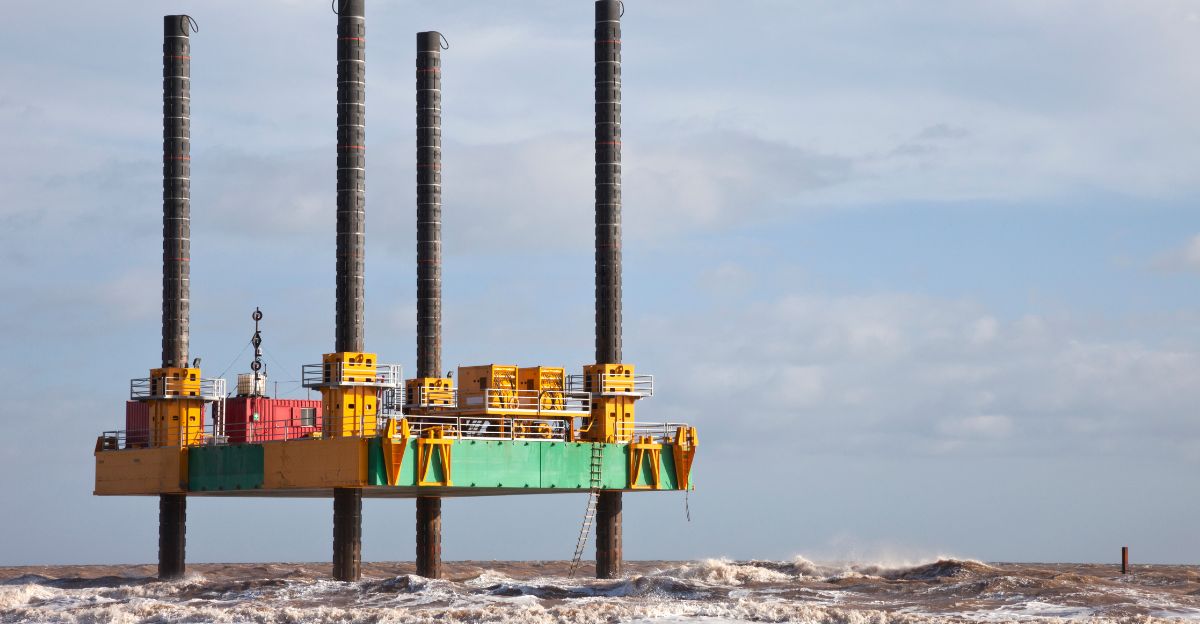

While this discovery is monumental, extracting lithium from the Salton Sea is not straightforward. The process involves drilling geothermal production wells thousands of feet below the earth’s surface to access lithium-rich brine. Once extracted, this brine must be pumped back underground, complicating operations further.
Environmental Concerns

The extraction process presents significant environmental and logistical challenges. For instance, it requires vast amounts of water, which could strain the already dwindling Colorado River—the region’s primary water source. Additionally, toxic dust particles from the receding lakebed contribute to high asthma rates among local residents, raising concerns about exacerbating health issues through large-scale mining operations.
Cultural Implications

Cultural concerns also arise from potential mining operations that could impact sacred Native American sites, including Obsidian Butte, which holds spiritual significance for local tribes. Pat Dobson, a staff scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, noted that “water consumption for the operation is a main impact,” highlighting another layer of complexity in balancing resource extraction with community needs.
Economic Opportunities for Imperial County

Imperial County stands to gain significantly from this lithium boom. With a median income of just $49,000 and nearly $257 billion projected annually in lithium carbonate revenue, according to a 2020 report by the California Energy Commission, local leaders are optimistic about economic revitalization. The county is already branding itself as “Lithium Valley,” planning to tax lithium extraction and allocate 80% of revenue to local projects.
Community Perspectives

Sara Griffen, executive director of the Imperial Valley Food Bank, expressed optimism about the future: “We need to be able to dream about this County and fully envision what it would look like if it were better for everyone.” However, community members remain cautious due to concerns over long-term environmental and social impacts associated with lithium mining.
A Double-Edged Sword

The Salton Sea’s lithium reserves represent a transformative opportunity for the U.S. to lead in the global clean energy race. Yet, harnessing this resource comes with significant challenges that must be addressed. From environmental risks to social equity concerns, navigating these complexities will be crucial as Imperial County embarks on this new chapter.
Global Implications

The implications extend beyond local communities; they resonate on a global scale as countries seek sustainable energy solutions. The U.S.’s ability to produce its own lithium could shift dynamics in international trade and reduce dependence on foreign sources, particularly China.
Looking Ahead

As companies like EnergySource Minerals prepare to begin mining operations as early as 2025, all eyes will be on how these developments unfold. The balance between economic growth and environmental preservation will be critical in determining whether this “white gold” can deliver on its promise.
Hope and Caution

For now, the Salton Sea remains a symbol of both hope and caution—a reminder that while opportunities abound in pursuing sustainable energy solutions, careful consideration must be given to their broader impacts on communities and ecosystems alike. The road to a sustainable future is rarely straightforward; thus, vigilance will be essential as this story continues to evolve.
Explore more of our trending stories and hit Follow to keep them coming to your feed!
Don’t miss out on more stories like this! Hit the Follow button at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest news. Share your thoughts in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!







