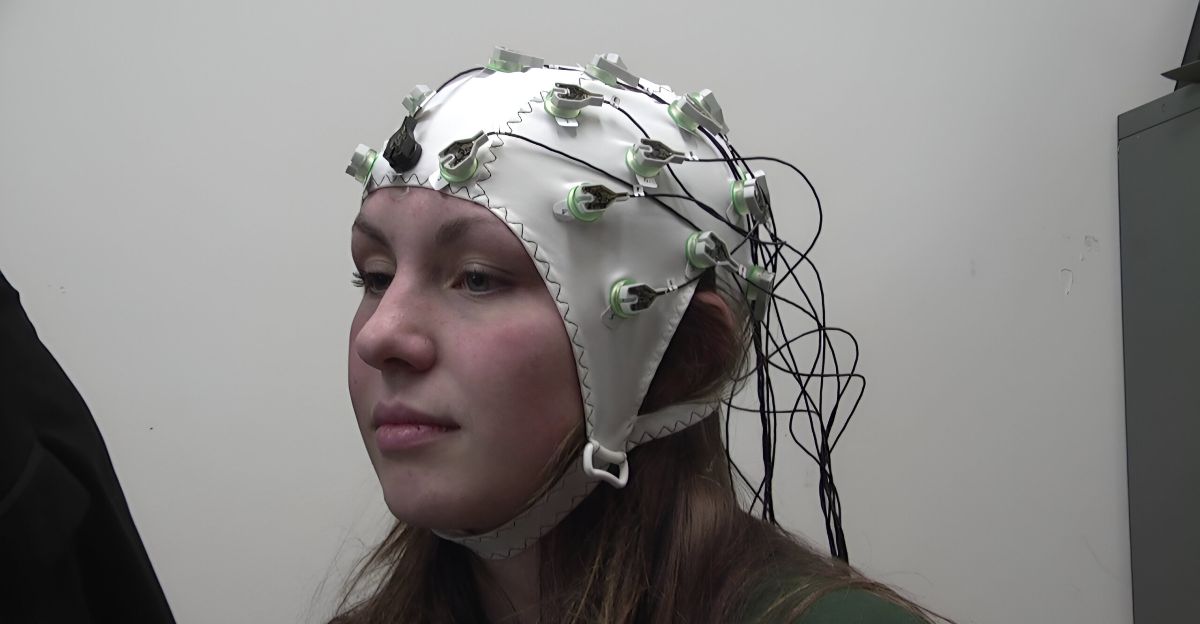

Can you imagine what it would be like to have a parasite quietly living in your brain, potentially influencing your thoughts, behaviors, and even your health, all without you realizing it? Studies have found that up to 30% of Americans might be infected with Toxoplasma gondii, a microscopic parasite often transmitted through undercooked meat or contact with cat feces.
Although most infected people show no obvious symptoms, mounting evidence indicates this hidden invader could have significant, wide-ranging effects. The story doesn’t end with the infection; it can trigger a chain reaction impacting everything from mental health to public policy. This is how this silent epidemic can quietly influence life across America.
Why It’s Happening
Toxoplasma gondii flourishes in places where people consume undercooked meat and where cats roam freely. This parasite’s egg can survive in soil, water, or on unwashed fruits and vegetables, making exposure surprisingly common.
In most cases, infections occur without noticeable symptoms, which allows the parasite to remain undetected for years. As urbanization grows and food safety standards change, the chances of this parasite spreading increase.
Subtle Neurological Effects

Once this parasite reaches the brain, it can interfere with how neurons and support cells communicate, subtly altering brain chemistry. Studies have shown that even low-level infections can impact neurotransmitter release and brain signaling.
These microscopic changes are invisible, but they could influence everything from your memory to your mood, potentially leading to more noticeable effects over time. The true scope of these neurological ripples is only beginning to be understood.
Behavioral and Personality Changes
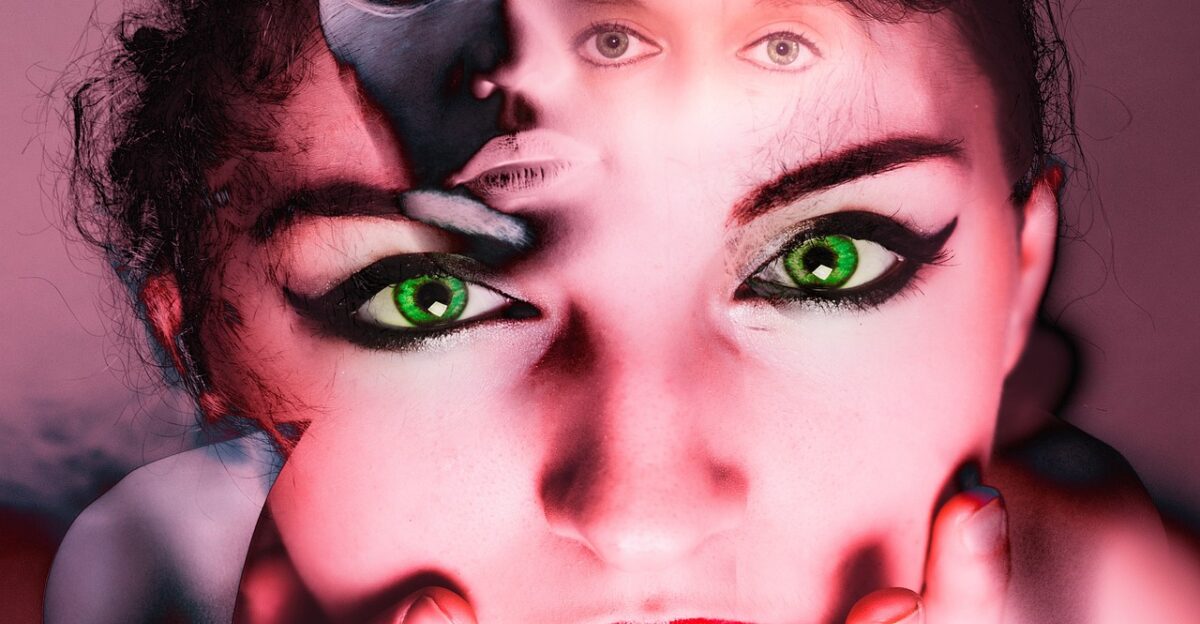

Researchers have found links between T. gondii infections and changes in behavior, including increased risk-taking, impulsivity, and differences in social behavior.
Some studies have also shown higher rates of mental health disorders like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in infected individuals. Although the precise reasons are still under investigation, the parasite’s impact on neurotransmitters like dopamine suggests that it could influence personality and decision-making.
Public Health and Mental Health Concerns

With potentially millions of people infected with this parasite, public health experts are raising concerns about the broader effects of T. gondii. Its possible links to mental illness and behavioral changes have raised concerns about its role in society’s well-being.
Since there’s no cure for chronic infection, the focus shifts to prevention and education. Mental health professionals are now also starting to look at T. gondii exposure as a potential factor in unexplained psychiatric symptoms.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations

This infection can be especially devastating for pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals. When it comes to pregnancy, T. gondii could cause miscarriage, stillbirth, or severe birth defects. People with weakened immune systems are also at risk of life-threatening brain and eye infections.
These severe outcomes emphasize the importance of awareness and prevention, particularly among vulnerable groups. The impact goes far beyond individuals; it affects families, healthcare providers, and entire communities.
Food Industry and Pet Ownership

The food industry is under increasing pressure to implement stricter meat safety standards, and pet owners are encouraged to adopt better hygiene practices. Cooking meat thoroughly and managing cat litter safely can significantly reduce your chances of infection.
Veterinarians and public health officials recommend keeping cats indoors and cleaning their litter boxes regularly. These simple changes could significantly decrease the parasite’s prevalence and help limit its impact on society.
Scientific and Medical Innovation
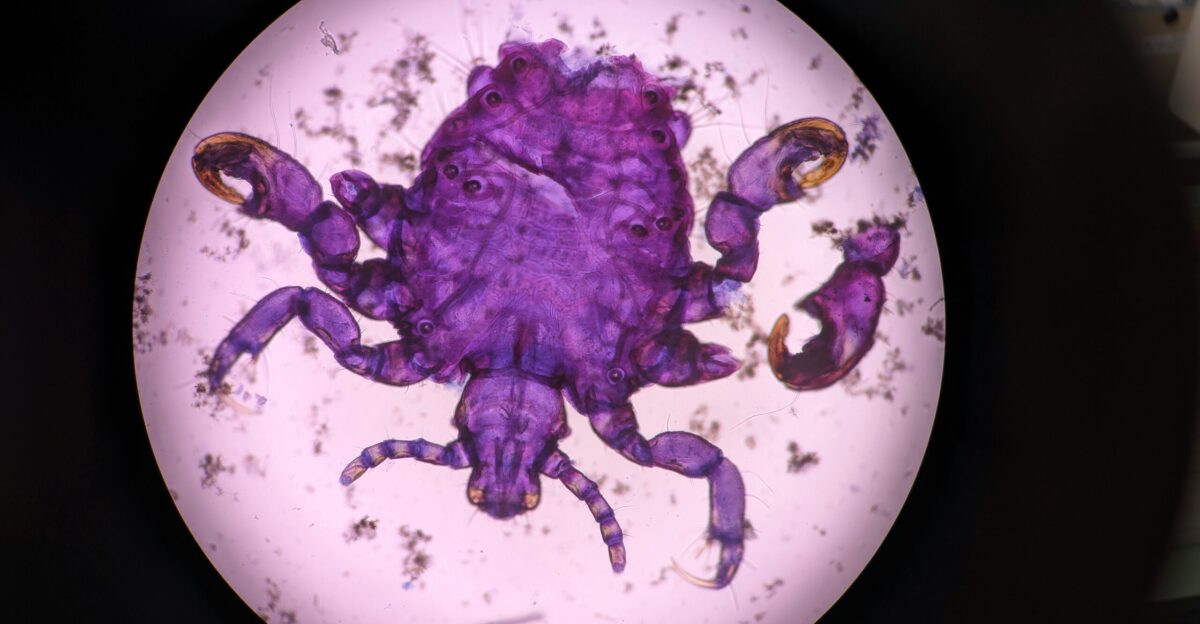

Interestingly, some scientists see potential in the parasite’s unique traits. Since it can cross the blood-brain barrier, researchers are investigating whether it could be used to deliver medications for neurological conditions.
While this concept is still in its early stages and carries its own set of risks, it shows how even a harmful parasite can inspire medical innovation.
What to Do Now

But what can you do right now? To protect yourself and those around you, always cook your meat to safe temperatures, wash your hands thoroughly after handling cats or gardening, and avoid unwashed produce. Pregnant women should delegate litter box duties and be extra careful around it. You can also kill the parasite by freezing your meat before you cook it.
These few steps can significantly reduce your risk of infection and will help you protect yourself and your loved ones from this harmful parasite.
Infecting Millions
Toxoplasma gondii is silently infecting millions of people around the world and could be shaping our brains, behaviors, and even society itself. As researchers learn more about its hidden influence, awareness and prevention are vital.
What started as an unnoticed infection could influence healthcare, food safety, and even public policy. The next time you sit down to eat or clean your beloved pet’s litter box, remember that a few simple steps can have significant consequences.







