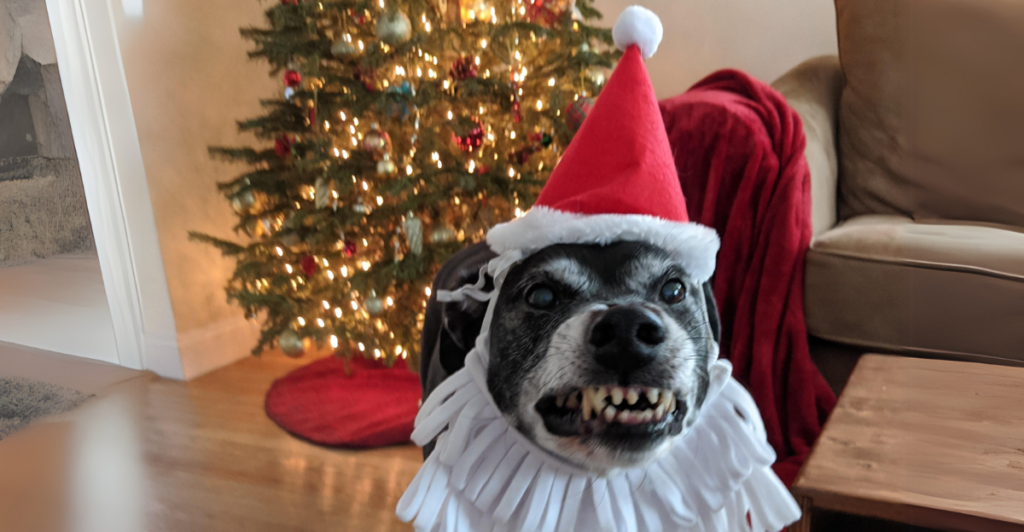

Dog ownership brings joy and companionship to millions worldwide. However, incidents where dogs exhibit aggression toward their owners are both alarming and perplexing. Understanding the underlying causes of such behavior is crucial for prevention and ensuring harmonious human-canine relationships.
Recent statistics highlight the significance of this issue. In the United States, approximately 4.5 million dog bites occur annually, with a notable portion involving familiar dogs and, in some cases, their owners. Alarmingly, children aged 5 to 9 are particularly susceptible, accounting for nearly 50% of reported cases.
Fear-Induced Aggression
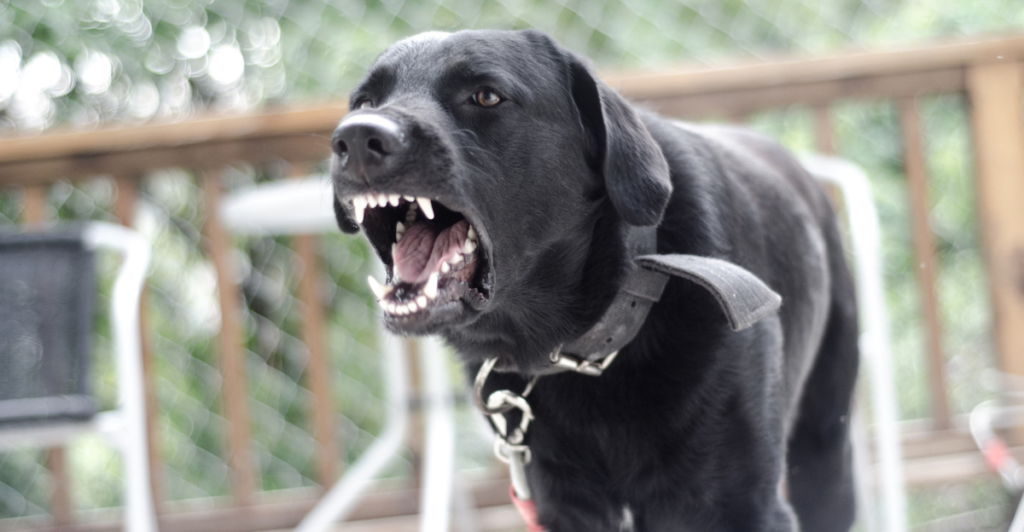

Fear is a predominant trigger for canine aggression. Dogs may bite when they perceive a threat, even from their owners, especially if previously subjected to negative experiences. Recognizing signs of fear, such as cowering, tucked tails, or avoidance, is essential. Proper socialization and positive reinforcement can help mitigate fear responses.
Territorial Behavior
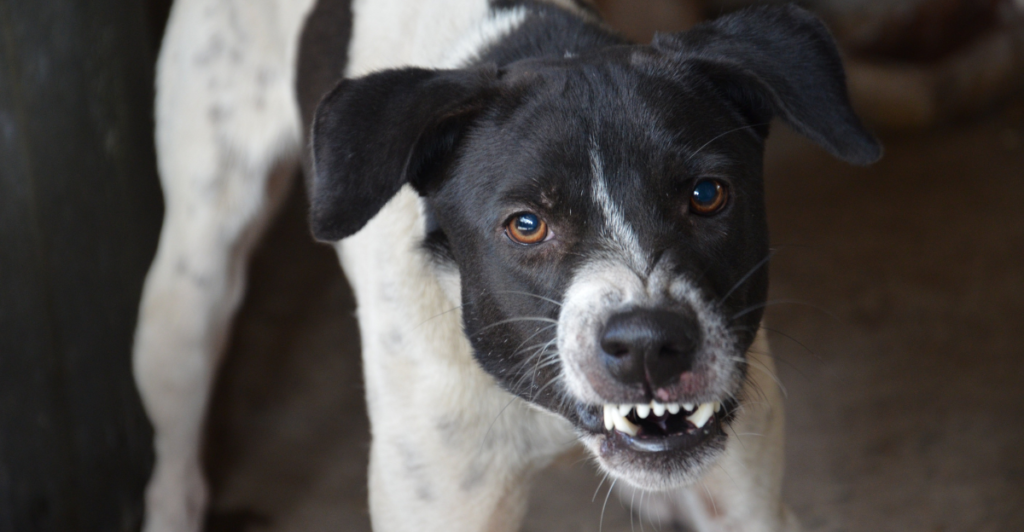

Dogs are inherently territorial creatures. They may exhibit aggression to protect their perceived domain, which can include their owners. Unfamiliar visitors or changes in the environment can trigger such responses. Establishing clear boundaries and gradual introductions to new stimuli can reduce territorial aggression.
Pain or Medical Issues
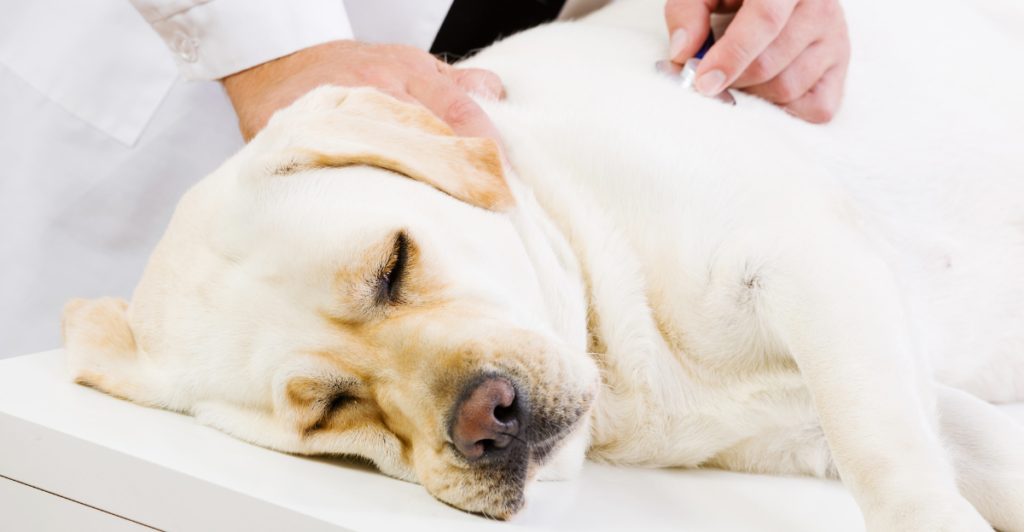
Undiagnosed medical conditions can lead to sudden behavioral changes in dogs. Pain, neurological disorders, or hormonal imbalances may cause irritability and aggression. Regular veterinary check-ups are vital to identify and address health-related behavioral issues promptly.
Lack of Socialization

Dogs that haven’t been adequately socialized may react aggressively to unfamiliar situations or people, including their owners. Early exposure to diverse environments, people, and other animals fosters adaptability and reduces fear-based aggression.
Resource Guarding

Resource guarding involves a dog becoming aggressive over possessions like food, toys, or sleeping areas. This behavior stems from an instinctual need to protect valuable resources. Training techniques that teach dogs to share and understand that their resources are not under threat can alleviate this issue.
Redirected Aggression

Sometimes, a dog may redirect its aggression toward its owner when unable to reach the source of its frustration, such as another animal. This can occur during heightened arousal states. Managing a dog’s environment to prevent overstimulation and teaching impulse control are effective preventive measures.
Dominance Issues

While the concept of dominance in dogs is often misunderstood, some may exhibit aggression when attempting to assert control. It’s essential to establish consistent training routines that promote cooperative behavior rather than confrontational dominance.
Anxiety and Stress

Chronic anxiety or stress can lead to aggressive behaviors in dogs. Factors contributing to canine stress include environmental changes, lack of mental stimulation, or separation anxiety. Providing a stable environment, regular exercise, and mental enrichment can help alleviate stress-induced aggression.
Previous Trauma or Abuse
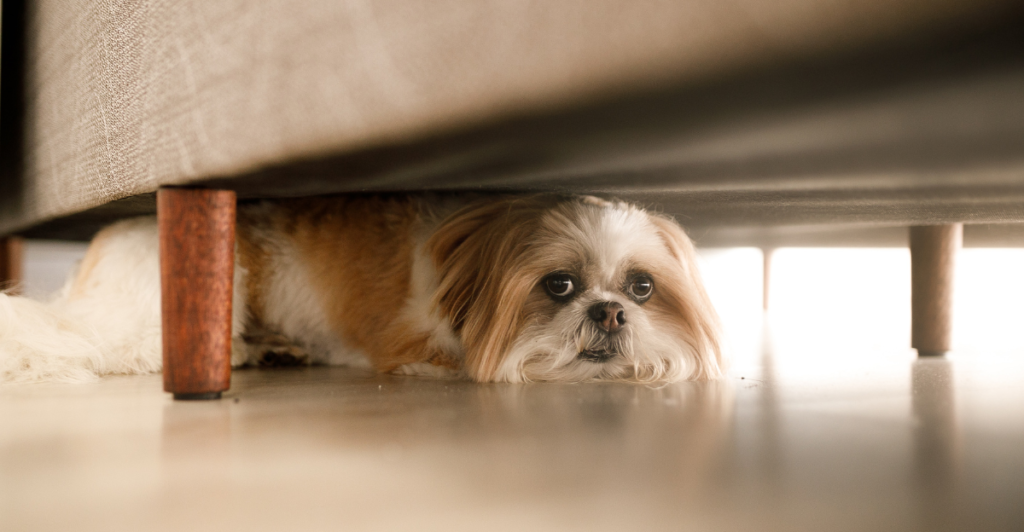

Dogs with histories of abuse or neglect may have deep-seated fears leading to aggression, even toward well-meaning owners. Patience, gentle handling, and, in some cases, professional behavioral therapy are necessary to rebuild trust and modify aggressive tendencies.
Inconsistent Training Methods
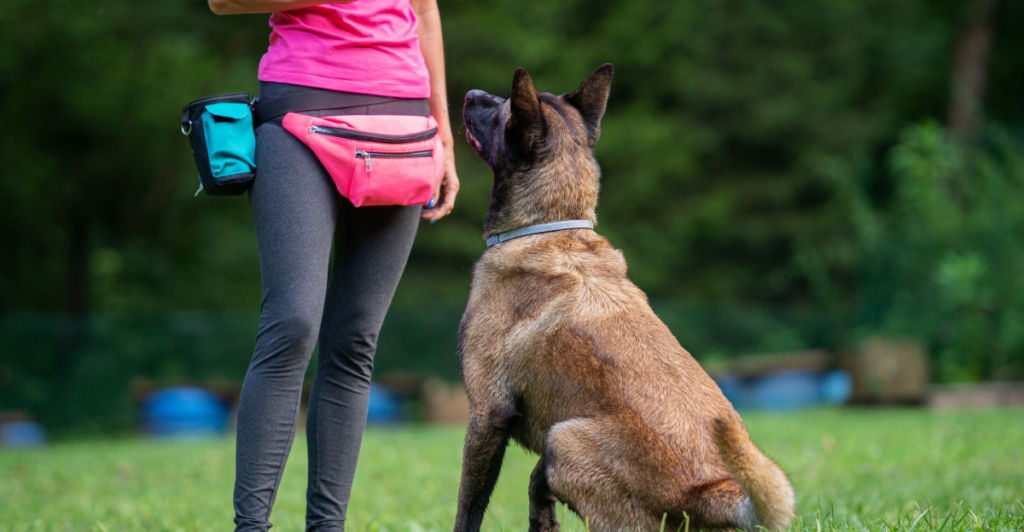

Inconsistent or harsh training methods can confuse dogs, leading to frustration and potential aggression. Employing positive reinforcement techniques and maintaining consistency in commands and expectations fosters a trusting and obedient canine companion.
Preventive Measures
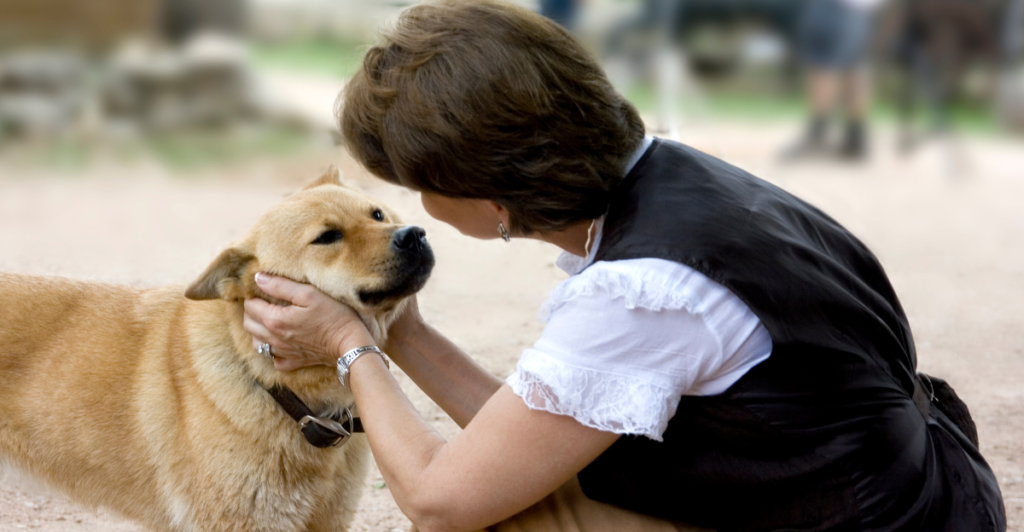

Preventing owner-directed aggression involves a multifaceted approach. Here are some methods you can try on your dog. Early Socialization will introduce puppies to various environments, people, and other animals during their critical developmental stages to build confidence and adaptability. Maintain regular Veterinary Care to ensure dogs receive routine health check-ups to identify and treat medical conditions that could influence behavior. Try Positive Reinforcement Training and utilize reward-based training methods to encourage desirable behaviors and strengthen the human-canine bond. Most importantly recognize and respect boundaries and learn to identify signs of discomfort or stress in your dog and adjust interactions accordingly to prevent escalation.
Mans Best Friend For A Reason
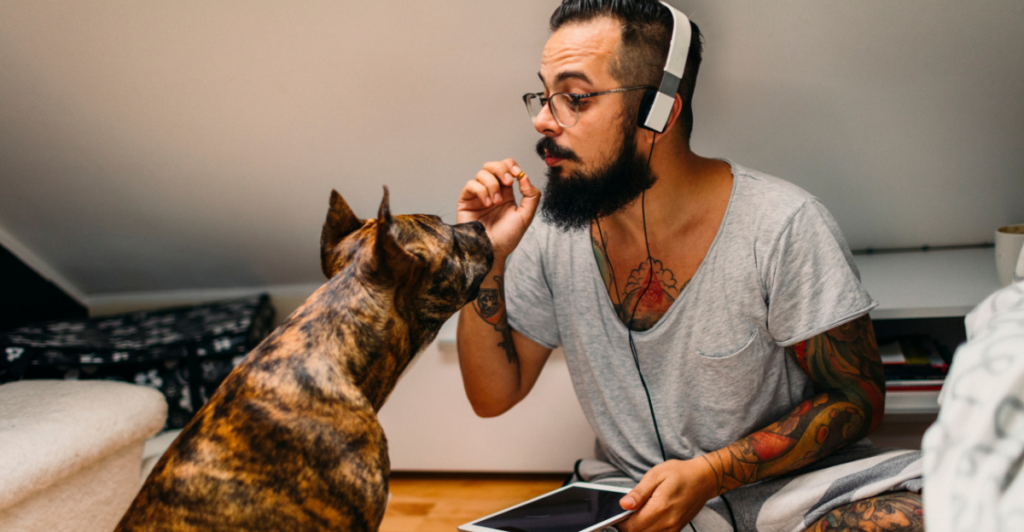

Understanding the reasons behind canine aggression toward owners is essential for prevention and fostering a safe, loving relationship. By recognizing the signs and implementing appropriate training and care strategies, owners can mitigate risks and ensure their dogs remain loyal and friendly companions.
In essence, responsible dog ownership encompasses more than meeting physical needs; it requires attentiveness to behavioral cues, consistent training, and a commitment to understanding and nurturing the psychological well-being of our canine friends.
Discover more of our trending stories and follow us to keep them appearing in your feed.

Meet the Massive Crocodiles That Make Their Homes 40 Feet Underground
13 Ways Dogs Are Helping Humans Live Longer, According to New Research
10 Most Difficult Dog Breeds – How an Untrained Dog Becomes a Dangerous Dog
12 Smartest Dog Breeds in The World and How They Can Help You
Stay connected with us for more stories like this! Follow us to get the latest updates or hit the Follow button at the top of this article, and let us know what you think by leaving your feedback below. We’d love to hear from you!







